Andrew McGregor
May 5, 2011
In the remote mountains that range along Libya’s western border with Tunisia, North Africa’s indigenous Berber tribes are locked in a life-and-death struggle with Mu’ammar Qaddafi’s Arab-supremacist regime. Though they were among the first to rebel against Qaddafi’s government, the Berbers are poorly armed and severely short of food and fuel with loyalist forces in the plains cutting off supply routes. Direct military intervention by NATO warplanes appears to the Berbers to be the only way of repelling advancing loyalist troops.
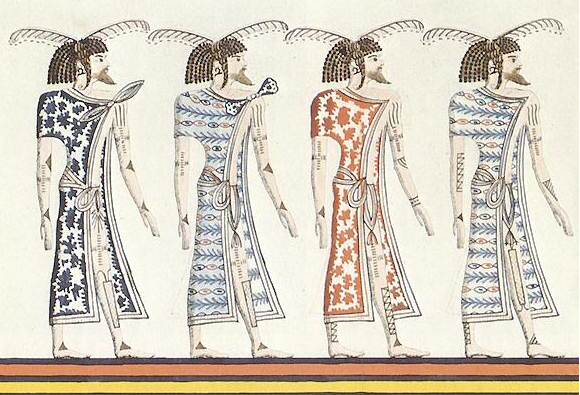 Heavily tattooed ancient Libu as depicted in a 19th Dynasty Egyptian Tomb Painting
Heavily tattooed ancient Libu as depicted in a 19th Dynasty Egyptian Tomb Painting
There are an estimated 25 million Berbers (as defined by use of Berber languages) spread across North Africa. The Berbers call themselves Imazighen (“Free Men”) and their ancestors were known to their ancient Egyptian neighbors as the Libu, the Meshwesh, the Tjehenu and the Tamahu.
Libya’s Berbers do not form a single group; a division between Eastern and Western Berbers dates back to ancient times and the desert-dwelling ethnic-Berber Tuareg developed their own independent culture centuries ago. As a result, there are three main groups of ethnic-Berbers in Libya with only minimal interrelation:
• The Western Berbers consist of two main groups.
1) The tribes of the Ait Willul live in the coastal city of Zuwara, known in Berber as Tamurt n Wat Willul (Town of the Ait Willul). Zuwara rose in revolt in February, but government forces suppressed the rebellion there a month later.
2) The Nafusa tribes live in the Western Mountains (al-Jabal al-Gharbi), better known as the Nafusa Mountains after the region’s Berber name, Adrar n Infusen. The Nafusa Berbers retreated there from the coast to isolate themselves from the mass Arabization of the Libyans after the arrival of two large Arab tribes in the 11th century, the Banu Hilal and the Banu Salim. The Nafusa declared against Qaddafi in the earliest days of the rebellion despite having little ability to defend their communities. With the government having managed to consolidate itself in other parts of western Libya, loyalist forces have now turned their attention to the mountain rebels.
• The Eastern Berbers live in the oasis towns of Jalu and Awjilah, about 250km southeast of the battlefront at Ajdabiya. Rebel sources reported a new loyalist offensive by troops in trucks mounted with anti-aircraft guns and Grad rockets against the settlements this week, part of a government effort to cut off rebel-held northern Cyrenaica from the oil and water-rich Libyan interior. The loyalist column of 45 vehicles was destroyed in a NATO airstrike on May 1 after the column attacked Jalu and Awjilah (Reuters, May 1; Upstream Online, May 2).
• The Tuareg live in communities focused on the oases of southwestern Libya. Though ethnically Berber, the Tuareg developed their own culture and version of the Berber language (Tamasheq or Tamahaq) after their ancestors migrated deep into the African interior roughly 1600 years ago. Despite insisting the Tuareg are actually Arabs, Qaddafi has also sought their favor at times due to their reputation as skilled desert fighters he could use in his efforts to expand his influence in the Sahara and Sahel regions. Qaddafi’s occasional efforts to champion the Tuareg cause and arm Tuareg rebel movements outside Libya appear to have brought large numbers of Tuareg from Mali and Niger to Libya to join the loyalist forces, though this recruitment has been achieved more through cash payments than personal loyalty to Qaddafi. [1] Libya’s own Tuareg appear divided on whether to support Qaddafi, though few, if any, appear to have joined the armed rebellion.
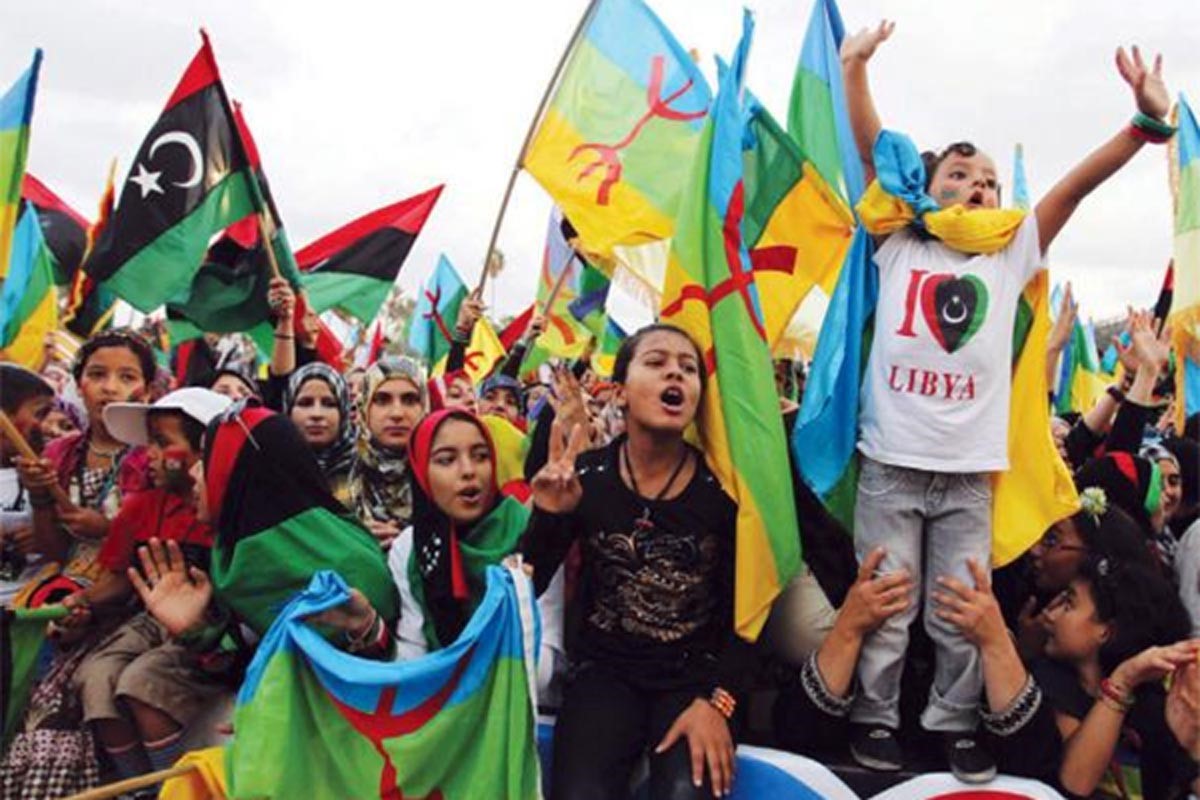 Modern Libyan Berbers Demanding Language Rights
Modern Libyan Berbers Demanding Language Rights
Qaddafi has always regarded the existence of the Berbers as an annoying reminder of the Berber origins of his own Arabized tribe and hence an impediment to his efforts to become leader of the pan-Arab community. An apparent softening of the regime’s approach to the Berber minority led by Sa’if al-Islam Qaddafi in 2007 (which included lifting the ban on Berber names) was reversed by Mu’ammar Qaddafi less than a year later when the Libyan leader travelled to the Western mountains to warn Berbers; “You can call yourselves whatever you want inside your homes – Berbers, Children of Satan, whatever – but you are only Libyans when you leave your homes” [2]
Notes:
1. See Andrew McGregor, “Libyan Loyalists and Dissidents Vie for Tuareg Fighters,” Terrorism Monitor Brief, March 10, 2011.
2. U.S. Embassy Tripoli cable 08TRIPOLI530, July 3, 2008, published by the Telegraph, January 31, 2011. See also AFP, August 24, 2007.
This article first appeared in the May 5, 2011 issue of the Jamestown Foundation’s Terrorism Monitor.
