Andrew McGregor
Central Asia-Caucasus Analyst, John Hopkins University
November 20, 2002
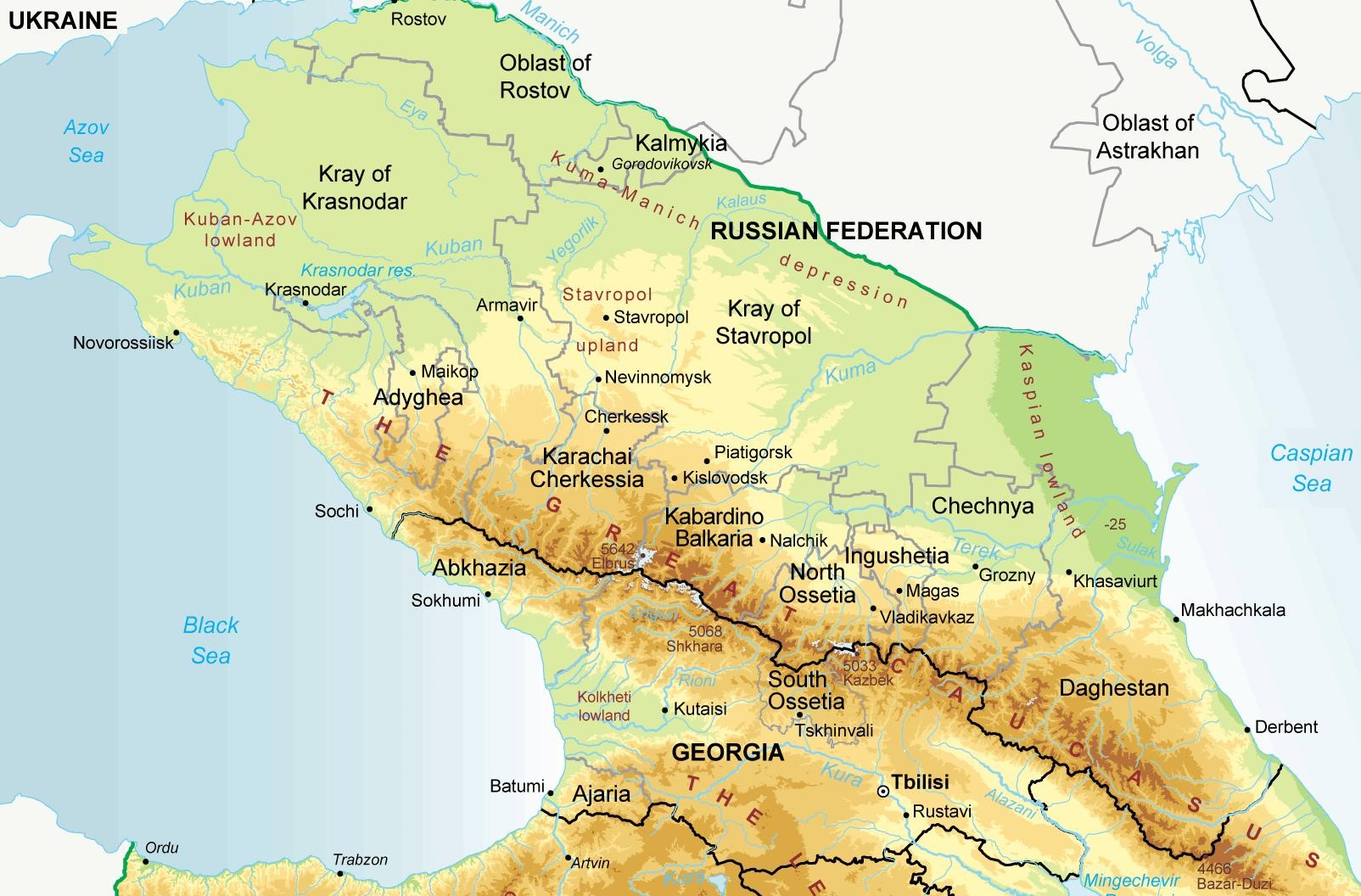
In the courts of several southern Russian cities a series of sensational trials has described ‘an attempted seizure of power’ by Islamists in the republics of Karachai-Cherkessia and Kabardino-Balkaria. Though strong ethnic tensions exist between the Cherkess, the related Kabards, and the Turkic Balkars and the Karachai, most conflict in the region has until now been politically or economically motivated. This fact, combined with the traditionally mild interpretation of Islam practiced in the region, made revelations of a violent attempt to overthrow the Russian state in favor of an Islamic Caliphate highly perplexing. Critics of the trials suggest that the proceedings were unfair and that the conspiracies are creations of the FSB and Russian prosecutors.
In 1996-99 jama’at-s (religious communities) began to be set up in Karachai-Cherkessia, centred on Imam Ramazan Borlakov’s mosque in Uchkeken. Borlakov was aided by Achimez Gochiyayev and Ibragim Bairamkulov, allegedly using funds supplied by Chechen warlord Shamil Basayev, Saudi mujahidin leader Ibn al-Khattab, and Dagestani Wahhabist leader Bagaudin Magomedov. Borlakov recruited a poorly educated but highly energetic young man, Khyzyr Salpagarov, who quickly became the leader of a Karachai jama’at. Salpagarov’s militancy was reinforced by attendance at one of al-Khattab’s guerrilla training camps in Chechnya in 1998. Borlakov, a charismatic speaker, attracted many to hear his militant sermons. By 1998 there were reports of Islamic missionaries from Syria, Jordan and Saudi Arabia spreading ‘Wahhabi’ beliefs, and cash, through the northwest Caucasus. The term ‘Wahhabi’ is used in Russia to describe any Sunni revivalist movement, regardless of their actual ties to the Wahhabi homeland of Saudi Arabia.
In the fall of 2001, Russian Prosecutor-General Vladimir Ustinov announced that investigators had uncovered a ‘Wahhabi’ group that intended to stage a coup d’état, and assassinate government officials in Karachai-Cherkessia and Kabardino-Balkaria. It was alleged that the 11 suspects had received military training from Arab commanders in Chechnya, and were working with ‘foreign Islamic organizations’. Security officials in the republics were puzzled by the case brought by federal authorities; one even responded that ‘to suggest that the 11 arrested men were preparing a rebellion in Kabardino-Balkaria, one of the most stable republics in the Federation, is like claiming someone is going to fly to the moon on a balloon.’ The head of the North Caucasus organized crime unit revealed that ‘investigations have yielded no evidence as to their aims, nor is there any clear definition of their activities. The statement that they were preparing a coup is groundless’. All the accused were ethnic Karachai and Balkars, leading to accusations that the charges were politically motivated by leading Cherkess individuals.
Salpagarov and 16 others were tried earlier this year for plotting to seize power. On the dock, Salpagarov outlined a plot in which his tiny jama’at group would lead an armed uprising to create an Islamic Caliphate across the northern Caucasus with the aid of Ruslan Gelayev’s Chechen guerrilla group. He further claimed that his jama’at had received $2 million from al-Khattab for the 1999 bombings in Moscow and Volgodonsk. Most of Salpagarov’s fellow defendants maintained that they were innocent and being persecuted for their religious faith. Russian sources claim that Salpagarov’s version of events has since been confirmed in the interrogation of Adam Dekkushev, another alleged conspirator extradited from Georgia in July of this year.
IMPLICATIONS:
Other trials of Cherkess, Balkar and Karachai defendants have convicted about thirty people this year for offences such as conspiracy to overthrow the state, membership in illegal armed formations, staging terror attacks, and murder. Many were found guilty for a wave of bombings that the Northern Caucasus experienced over the last three years. The convictions represent part of a much larger problem in the Russian Federation – of over 2000 bombings in the Federation in the last three years, only 15% have been attributed to terrorists.
Many of the defendants were accused of receiving military and ideological training at so-called ‘Taliban training-camps’ in Chechnya. Gochiyayev, who is still at large, has been accused by the FSB of responsibility for the 1999 apartment block bombings in Russia. Several of his alleged accomplices have since been killed fighting Russian forces in Chechnya. Gochiyayev has stated that he was framed in an FSB operation to blow up the buildings to create pro-war sentiment in Russia.
The arsenal that the plotters were allegedly intending to use included two grenade launchers, a dozen rifles, two submachine guns, and a handful of grenades. It was barely enough to equip the conspirators, and was certainly inadequate to arm supporters. Several of the suspects were underage at the time of their offences; others were claimed to be vagrants or outpatients at local psychiatric hospitals. For the time being several of the leaders of the alleged plot remain at large, including Borlakov and Bairamkulov. Shamyl Basayev is about to be tried by a Chechen Shari’a court for his role in the October hostage-taking in Moscow.
The trials of the young militants were conducted in strict secrecy. Defence lawyers charge that the secrecy was required since the conspiracy charges were baseless and without evidence. Some proceedings were conducted amidst charges that the defendants had been tortured during interrogation. Stavropol newspapers unsuccessfully protested the secrecy as a violation of the Russian constitution and criminal code.
CONCLUSION:
For many young people, Islamism offers an alternative to the corruption and ethnic dissonance that dominates the North Caucasus. In this sense, the conspiracy charges may be regarded as more pre-emptive than punitive. One of the more bizarre theories behind the conspiracy charges suggests the involvement of Western security agencies in promoting Wahhabism as a means to the secession of the North Caucasus from Russia. More plausible is the suggestion that state authorities have promoted the Wahhabist threat to counter attention to their own corruption. Unlike the zeal with which the Islamists have been prosecuted, there have been few arrests and fewer convictions in ongoing political violence in Karachai-Cherkessia. In the last year alone, three leading politicians have been assassinated and the chairman of the Supreme Court nearly killed. This violence has little to do with Islam, but is rather the result of different clans battling for control of the republic’s resources.
Ethnic discord and a general crackdown on Islamic activities have fostered an atmosphere in which otherwise improbable accusations are easily believed. Shrinking democracy, declining economic prospects and the growing influence of military and security figures in local politics contribute to the radicalization of young people in the northwest Caucasus. According to Circassian author Amjad Jaimoukha, ‘the authorities must provide the young men with hope and a decent living, so as not to be attracted to extremism. With the oppression of national culture and traditions, the youth are turning to foreign ideas that are undermining the fabric of society.’ There is no doubt that the Russian authorities are alarmed by the appeal of jama’at organizations to disaffected youth from all the major nationalities of the northwest Caucasus. While federal authorities have exaggerated the threat posed by such groups at present, the recent trials suggest that the use of Soviet style methods remain a useful tool in the ongoing consolidation of the Russian Federation.