Andrew McGregor
Eurasia Daily Monitor
September 11, 2023
In recent days, waves of Russian drones have attacked the Ukrainian port of Izmail, a major outlet for Ukraine’s grain (al-Jazeera, September 4). Such assaults on food infrastructure alarm the leadership of drought-suffering parts of Africa reliant on exports of Ukrainian grain and complicate the Kremlin’s efforts to expand Russian influence on the resource-rich continent.
 Under the guidance of President Vladimir Putin, Moscow’s campaign is pitting Russian interests in the region against those of the West, a rivalry in some ways reminiscent of the Cold War competition over Africa, though the Kremlin has developed a new and less accountable approach by deploying the private Wagner network of security forces, opinion manipulators and resource development firms. The long-term success of Russian efforts in Africa will depend in large part upon the establishment of a secure Russian naval port, preferably on the African coast of the strategic Red Sea. To create such a port, Russia must address historic foreign policy failures.
Under the guidance of President Vladimir Putin, Moscow’s campaign is pitting Russian interests in the region against those of the West, a rivalry in some ways reminiscent of the Cold War competition over Africa, though the Kremlin has developed a new and less accountable approach by deploying the private Wagner network of security forces, opinion manipulators and resource development firms. The long-term success of Russian efforts in Africa will depend in large part upon the establishment of a secure Russian naval port, preferably on the African coast of the strategic Red Sea. To create such a port, Russia must address historic foreign policy failures.
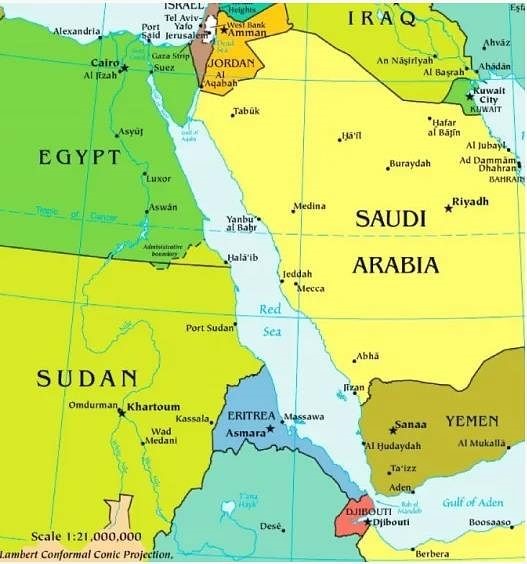
When the Suez Canal opened in 1869, it created new strategic opportunities for European powers. Great Britain, with an ambitious mercantile class supported by the world’s most powerful navy, took immediate steps to establish a chain of ports through the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean, allowing the wealth of its rich Asian dominions to flow freely to the center of the Empire. France and Italy followed, establishing their own bases in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden to facilitate access to their own colonies. Imperial Russia, a northern empire in a perpetual search for warm-water ports, was slow to see the opportunities presented by the canal, leaving it to an odd group of privately-backed Cossacks and Orthodox priests to try to establish an African colony in Djibouti on the Gulf of Aden in 1889. “New Moscow,” established on land already claimed by France, was quickly destroyed by a French naval bombardment.
 Destruction of the Russian Baltic Fleet at the Hands of the Japanese, 1905
Destruction of the Russian Baltic Fleet at the Hands of the Japanese, 1905
The diplomatic crisis that followed sapped Russian enthusiasm for African adventures, though Cossack missions continued to reach the Ethiopian emperor, who controlled what is now modern Eritrea, including the Red Sea ports of Massawa and Assab. By the time of the Russo-Japanese War, the significance of Russia’s failure to establish a Red Sea or Indian Ocean port was exposed when its Baltic fleet was forced to make an 18,000-mile voyage to the Sea of Japan without resort to proper coaling and repair facilities. The lesson of the exhausted fleet’s total destruction by the Japanese when it finally arrived was understood by the Soviets, who focused on the establishment of warm-water ports to support naval operations in the Indian Ocean and South-East Asia in the 1960s and 70s.
The collapse of the Soviet Union brought a temporary end to Russia’s presence overseas, but the neo-Soviet ambitions of Vladimir Putin have revived the campaign to expand Russian military and commercial influence in Africa. Key to this is the establishment of a port on the strategically important Red Sea, the two most likely hosts being Sudan and Eritrea, nations that are similarly at odds with the West.
Khartoum was engaged in talks with Moscow over the establishment of a Russian naval base on Sudanese territory up to the outbreak of clashes between rival wings of the Sudanese military in April 2023. Now, with the ongoing turmoil within the country, Moscow’s focus has shifted to Eritrea, a stable but totalitarian state accused of significant human rights violations and crimes against humanity.
Eritrea is currently ruled by 77-year-old President Isaias Afwerki, and has not had an election since achieving independence in 1993. In terms of both prosperity and civil freedoms, the country ranks near the bottom in both categories; many citizens are reliant on remittances from Eritrean expatriates to obtain basic necessities. Many of the expats have fled Eritrea to escape mandatory conscription for indefinite periods and other hardships. Even so, the regime’s agents abroad continue to try to control their lives through taxation, threats to family members and other measures.
In the early years of its independence, Eritrea enjoyed a congenial relationship with the United States. However, tensions arising from the 1998-2000 border war with Ethiopia led to a rift with Washington and a shift away from democratic norms and regional cooperation in favor of xenophobic sentiments. All economic failings of the regime are attributed to the existence of UN and US sanctions, promoting anti-Americanism in a country with little access to independent news sources. Eritrea is thus viewed in Washington as a destabilizing influence in the Horn of Africa and a possible partner of both Russia and Iran. Moscow now favors removing the UN sanctions on Eritrea, but doing so will require the support of nine members of the Security Council, including all five permanent members.
Eritrea has repaid this diplomatic support by being one of only five countries to vote against the March 2022 UN resolution condemning Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, joining Syria, North Korea, China and Belarus. During a visit in January to by Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov, his Eritrean counterpart, Osman Saleh, blamed the war in Ukraine on America’s “reckless policy of hegemony and containment that they have pursued in the past decades” (Ministry of Information – Eritrea, January 27).
 Eritrean President Isaias Afwerki
Eritrean President Isaias Afwerki
Eritrea’s relations with Russia have intensified of late; having never made a trip to Moscow since independence, Afwerki has already made two this year. A major topic of discussion has been the establishment of Russian naval facilities on Eritrea’s 700-mile Red Sea coast. The prime candidates for such facilities include the ports of Assab and Massawa.
During a July 28 meeting with Russian President Vladimir Putin on the sidelines of the second Russia-Africa Summit, Afwerki described Russia’s role in Ukraine as resistance to a NATO plot to rule the world: “The war declared by NATO on Russia is not only against Russia; its aim is to dominate the whole world… NATO is defunct. NATO does not exist. NATO is in intensive care… I think we need to strategize and I say Russia will have to lead this strategy. Russia will have to design a plan on facing this declared war, not only on Russia, but this is a global war. Everybody should come and join Russia in this strategy, and the sooner, the better” (Kremlin.ru, July 28).
Such enthusiasm for Russian leadership was in short supply at this year’s Russia-Africa Summit, which saw a significant drop-off in attendance by African heads of state: from the 43 who attended the first summit in 2019, only 17 did so this year. The summit came ten days after Russia announced it was pulling out of the UN-brokered deal guaranteeing the safe passage of Ukrainian grain exports through the Black Sea to Africa. Putin’s pledge to ship limited amounts of free grain to six friendly African nations, including Eritrea, did little to appease those states not on the list. The contradictions between Moscow’s policy in the Black Sea and its ambitions in Africa were thus exposed in the midst of Russia’s influence offensive in Africa. To move forward with its plans in the Red Sea, Moscow will need to emphasize a Russian option to the alleged threat from the West to non-democratic states like Sudan and Eritrea.
