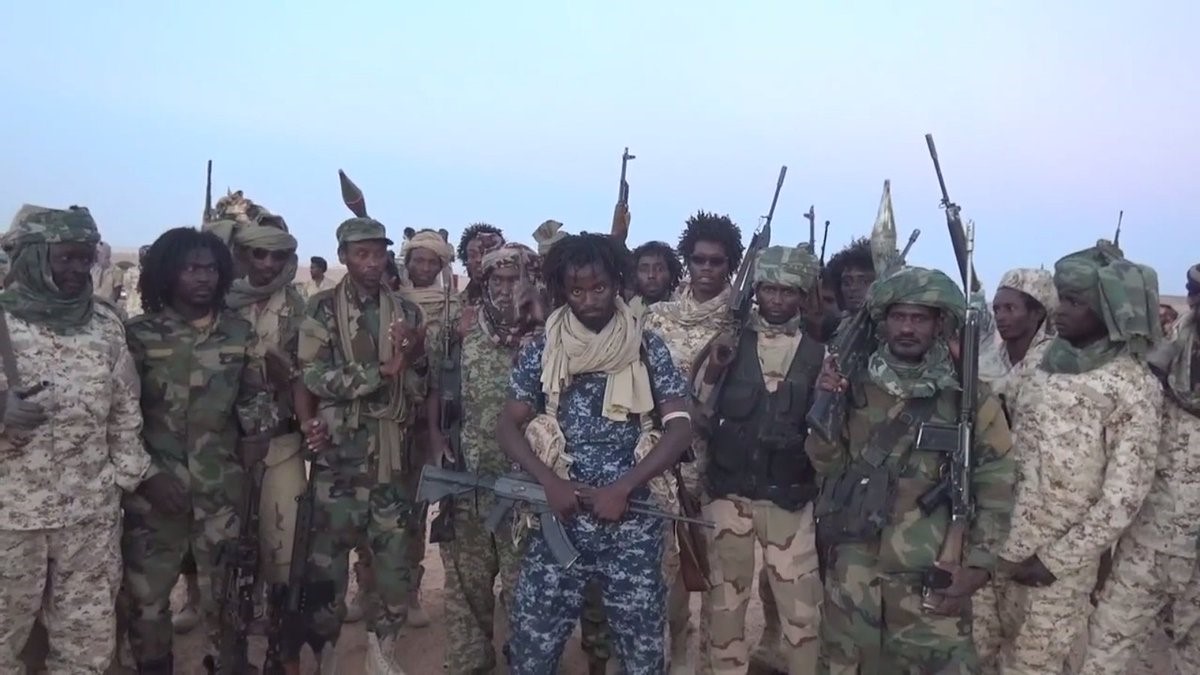
AIS Special Report, November 12, 2018
Andrew McGregor
Relative peace has reigned in northern Chad’s arid Borku-Ennedi-Tibesti (BET) region since 2009, when most of the insurgents seeking to end President Idris Déby Itno’s 28-year rule were driven north across the border into Libya. Some 11,000 Chadian rebels have worked as mercenaries for both sides of the Libyan conflict, accumulating arms, cash and military experience as they prepared to make their eventual return to Chad.
Dissident general Mahamat Mahdi Ali gathered many of these groups together under his leadership in the Front pour l’alternance et la concorde au Tchad (FACT – Front for Alternation and Concord in Chad). [1] The first formation to return to Chad is the Conseil de Commandement Militaire pour le Salut de la République (CCMSR – Military Command for the Salvation of the Republic), founded in March 2016 as a split from FACT. The CCMSR claims to have 4500 fighters, mostly Daza Tubu, with smaller numbers of Zaghawa, Arabs and Maba (the latter hailing from the east Chadian province of Wadai).
 Chad, with Tibesti in the North-West (Ezilon.com)
Chad, with Tibesti in the North-West (Ezilon.com)
President Déby, a skillful desert fighter and former Chadian Army commander, took power in a coup in 1990 and has been re-elected five times in disputed elections. Rebellions have been frequent, but in recent years Chad has become a major regional ally of France and the United States in the struggle against terrorism in the Sahara/Sahel region. It is a member of the French-sponsored G5S counter-terrorism alliance along with Mauritania, Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso, as well as the Multi-National Joint Task Force (MNJTF), fighting Boko Haram terrorists in the Lake Chad region. With its headquarters in the Chadian capital of N’Djamena, other MNJTF members include Cameroon, Nigeria, Benin and Niger. On October 10, Boko Haram elements crossed the border into Chad and attacked an ANT base at Kaiga Kindji, killing eight soldiers before being driven off with a reported loss of 48 militants.
In a November 2016 statement, CCMSR secretary-general Mahamat Hassane Boulmaye described the Déby regime as “a perfect illustration of clan despotism in its most pernicious and most abject form.” After outlining the administration’s corruption and use of violence against its opponents, Boulmaye justified the CCMSR’s insurrection: “Ours is the armed struggle. The vulgar despot of Chad maintains power by force; why is it so bad to drive him away by force? The path of armed struggle is the only one left, and it will overcome by the grace of God.” As for Déby, “He will have a double choice, the grave or the prison” (Lepythonnews, November 27, 2016).
The rebel leader also noted that many Zaghawa (Déby’s ethnic group) were abandoning the president; Boulmaye’s strategy was to encourage other Zaghawa to do the same by creating “a situation of insecurity” for members of the ethnic group. [2]
Return to Chad
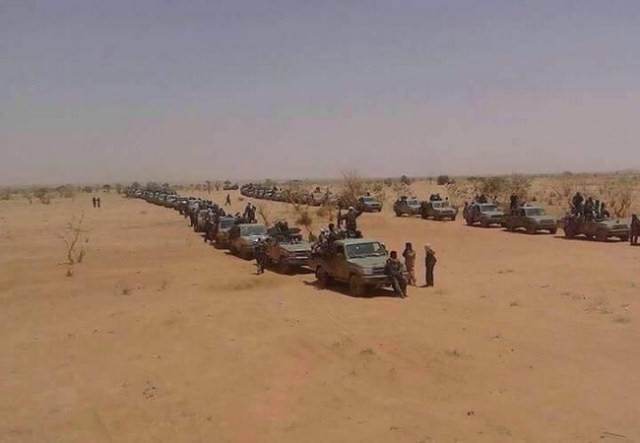 CCMSR Column in Northern Chad (Tchad Convergence)
CCMSR Column in Northern Chad (Tchad Convergence)
The CCMSR began to probe Chadian defenses in April 2017 with an attack inside Chad that killed 12 soldiers (RFI, August 14, 2018). A further clash with the Armée National du Tchad (ANT) took place on August 18, 2017, when a CCMSR column moving from Libya to Darfur ran into a Chadian Special Forces patrol at Tekro in the Ennedi region of northern Chad. Though small and without a permanent population, Tekro’s wells and airstrip make it strategically important. The Chadian unit suffered casualties, including the deaths of two colonels, while the survivors fled into the mountains (TchadConvergence, October 19, 2017).
Imprisoned Leadership
The movement has managed to survive despite the arrest of three leading members in Niger in October 2017, allegedly at the request of N’Djamena. Boulmaye, CCMSR spokesman Ahmat Yacoub Adam and CCMSR external affairs secretary Dr. Abderahman Issa Youssouf were extradited to Chad, where they were charged with the capital offense of terrorism and transferred to the notorious desert prison at Koro Toro. Supporters of the men appealed unsuccessfully for France to intervene against the extradition. France had previously granted refugee status to Boulmaye and Youssouf. Adam has refugee status in Egypt.
 Mahamat Hassane Boulmaye (left), Ahmat Yacoub Adam (center) and Dr. Abderahman Issa Yousouf (right) (Tchad Convergence)
Mahamat Hassane Boulmaye (left), Ahmat Yacoub Adam (center) and Dr. Abderahman Issa Yousouf (right) (Tchad Convergence)
Fearing the three would meet “certain death” if extradited to Chad, the CCMSR threatened to attack Niger in an October 25, 2017 statement, though the promised strike did not materialize (Tchad Convergence/Deutsche Welle, October 27, 2018).
Boulmaye’s temporary replacement as secretary general was Colonel Mahamat Tahir Acheick. The colonel was succeeded in 2018 by Hissène Habré loyalist Michelot Yogogombaye (a.k.a. Kingabé Ogouzeïmi de Tapol), who works from exile in Paris (Tchad Convergence, August 17, 2018; Tchad Convergence, April 3, 2018).
The Battle of Kouri Bougoudi
Chad closed its border with Libya in January 2018, but stood little chance of avoiding infiltration by the CCMSR along a lengthy and lightly inhabited stretch of inhospitable desert.
CCMSR militants attacked a military outpost at Kouri Bougoudi (35 km from the Libyan border) in the volcanic Tibesti region of northeastern Chad on August 11, 2018. The Tibesti Mountains, a picturesque but physically challenging area, is regarded as the ancestral homeland of the Tubu people of northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. The discovery of gold in Tibesti has brought artisanal gold miners from Niger, Sudan and other parts of Chad. Many are based around Kouri Bougoudi.
Arriving in over one hundred trucks at 2:23 AM, the assailants were armed with DShK “Dushka” 12.7 mm heavy machine guns and ZPU-4 quadruple barrel anti-aircraft weapons systems, using 14.5 mm KPV heavy machine guns. Both these Soviet-era designs are commonly mounted on the beds of 4×4 pick-up trucks in Libya and Chad.
A CCMSR statement released after the battle claimed 73 government troops killed and 45 taken prisoner (including three officers) against a cost of four CCMSR dead and seven wounded (Al Wihda [N’Djamena], August 19, 2018).
The attack was initially denied by the Minister of the Interior and Security, Ahmat Mahamat Bachir, who mocked CCMSR claims: “No attack on our position took place. I don’t know – did they attack the pebbles, the mountains?” (RFI, August 24, 2018). N’Djamena eventually acknowledged the death of Colonel Tahir Oly and two other soldiers in the clash (Al-Wihda [N’Djamena], August 12, 2018; Le Monde, September 14, 2018).
Reluctant to admit the political context of the attack on the village and its garrison, a Chadian security source told French media only that the army had been confronted by “coupeurs de route” (highwaymen) and “drug traffickers” (RFI, August 11, 2018). Two days later, the government ordered all gold miners to leave Kouri Bougoudi within 24 hours or face removal by force (Tchad Convergence/Xinhua, August 13, 2018). Chadian forces were ordered to destroy all the miners’ goods and equipment in land and air attacks (AFP, August 16, 2018).
A CCSMR statement released on August 17 suggested that the movement was willing to consider releasing their prisoners (including three officers identified by rank and name) to the Red Cross or Red Crescent once the three imprisoned CCSMR leaders were released “immediately, unconditionally [and] safe and sound” (RFI, August 17, 2018). According to the statement, three columns of CCSMR forces were now in Chad to end “its economic crisis and dictatorship” (Tchad Convergence, August 12, 2018). Minister of Public Security Ahmat Mahamat Bachir in turn rejected the possibility of making any kind of deal with “savage mercenaries, bandits [and] thugs” (Tchad Convergence, August 22, 2018).
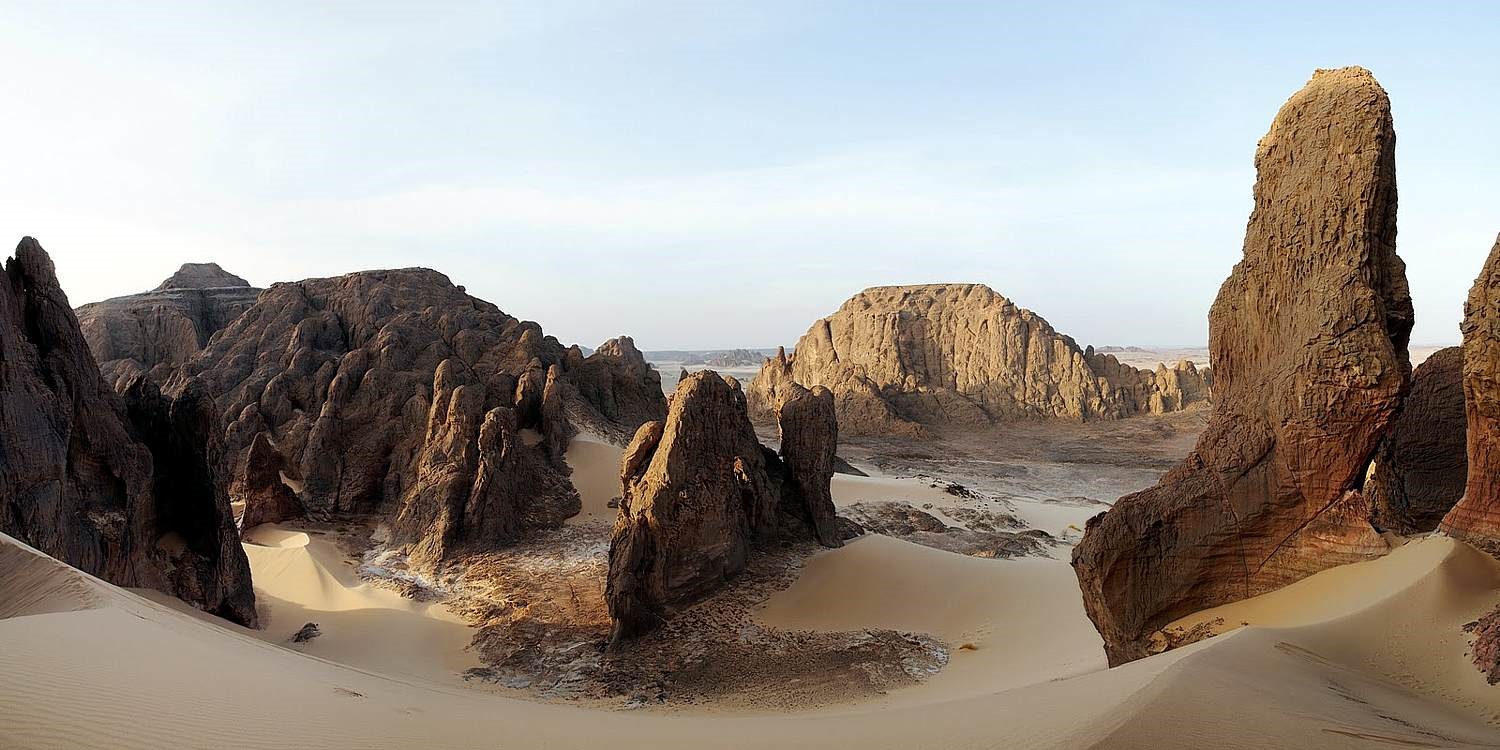 The Tibesti Mountains (Sakhalia.net)
The Tibesti Mountains (Sakhalia.net)
The CCMSR claimed to have routed Chadian troops in a second attack in the same area on August 22, but local sources claimed the government forces had evacuated quietly, leaving the region open for the return of illegal gold-miners (Tchad Convergence, August 22, 2018). Reports of this second attack were again refuted by the Interior Minister, who described them as “the false reports of mercenaries” (TchadInfo, August 22).
President Idriss Déby declared on August 20 that “the era of seizing power by arms” was forever over, adding that “clinging to warlike rhetoric” was “a suicidal option” (RFI, August 23, 2018). The CCMSR’s spokesman responded by noting that Chad had enjoyed ten years of relative peace since the last major effort to overturn Déby’s regime, but in that time the president had done nothing to establish an effective administration or improve the lot of Chadians: “[The president] thinks himself powerful, invincible, untouchable. But we will prove the opposite to him” (RFI, August 23, 2018).
On September 13, two Chadian helicopters bombed Kouri Bougoudi, where a number of miners had failed to obey the evacuation order (Le Monde, September 14, 2018). Retaliatory government bombing raids in Tibesti are alleged to have killed civilians while cluster bombs are reported to have been used to devastate the camel herds on which the traditional local economy is based (La Croix, September 6, 2018). The bombing did not prevent another attack on ANT forces at Tarbou on September 21.
Battle at Miski
The ANT clashed with insurgents again on October 24 at a place called Miski, which has only recently been administratively detached from Tibesti region and made part of the Borku region, to the great displeasure of many of Miski’s residents (Jeune Afrique/AFP, October 25, 2018). Responding to reports of civilian casualties, Chad’s Defense Minister, Bishara Issa Jadallah, insisted that there were no civilians left in Miski and that the attack had been entirely initiated by “drug traffickers” and “traffickers of human beings” (RFI, October 25, 2018).
In reaction, CCMSR spokesman Kingabé Ogouzeïmi de Tapol said his movement was “determined to drive these Mafia criminals [i.e. the Déby regime] out of Chad” and called for “a total and widespread popular insurgency” in Chad (CCMSR Press Release no. 0033, Facebook, October 24, 2018).
Driving the CCMSR from Libya
Residents of southern Libya Fezzan region have grown impatient with promises to clean up the south from both the Tripoli-based Government of National Accord (GNA), its Tobruk-based rival, the House of Representatives (HoR) and “Field Marshal” Khalifa Haftar’s so-called Libyan National Army (LNA). Armed locals have at times joined under-manned security operations in the south, most recently in mid-September when they joined an attack by the Salafist Khalid bin Walid Brigade on Chadian militants, freeing two hostages and killing six Chadians (Libya Herald, October 24, 2018; October 15, 2018).
The Khalid ibn al-Walid Brigade (aka the 104th Brigade), a mostly Tubu unit under the command of Yusuf Hussein Salah, has suffered recent losses fighting the Chadians; four fighters were killed in a clash on October 14, while a further six fighters who had been abducted were found dead four days later (Libya Observer, October 18, 2018; Libya Herald, October 15, 2018). In late October, the brigade was forced to abandon a siege of Chadian militant groups at a Chinese-built factory in the Fezzan’s Umm al-Aranib district, conceding that without further support from the LNA, the brigade was outmatched by the Chadians’ superior manpower and weaponry (Libya Observer, October 28, 2018). Qatar, a supporter of anti-Khalifa Haftar militias in Libya, has been accused of helping to finance the CCMSR (RFI, August 14, 2018).
Shortly after discussing security cooperation with President Déby in N’Djamena on October 16, Haftar launched a new LNA operation in the Fezzan’s Murzuq Basin in October to “cleanse the south of the country from criminal gangs and terrorist groups.” To accomplish this, he assembled a joint force of LNA units that included the 10th Infantry Brigade under Colonel Muhammad Baraka, the 181st Infantry Battalion under Tariq Hasnawi, the 116th Infantry Battalion and the Kufra-based Subul al-Salam Brigade (mostly Salafist Zuwaya Arabs) (Libya Herald, October 24, 2018; Libyan Address, October 19, 2018). A UN Security Council report recently claimed Subul al-Salam has defied its mandate to control human trafficking on the southern border to engage in the traffic themselves, holding migrants at the Himmaya forced-labor camp in Kufra. [3]
Forecast
Chad is undergoing a massive economic crisis based on the decline in oil prices in recent years. Opposition leaders are regularly detained, as are the leaders of a civil opposition movement, “Iyina” (Arabic – “We are tired”). While the defense budget was largely untouched, there have been cutbacks nearly everywhere else and civil servants have gone for months without wages. With Chad’s citizens asking what happened to all the oil revenues already received in what remains one of the world’s most poorly developed nations, Déby’s regime may find itself vulnerable to an armed movement seeking an end to the Déby government. Should the CCMSR gain traction in the north, a desperate N’Djamena might be forced to withdraw MNJTF forces from the Lake Chad Basin to tackle a more immediate threat to the capital.
Notes
- For Mahamat Mahdi Ali, see: “Rebel or Mercenary? A Profile of Chad’s General Mahamat Mahdi Ali,” Militant Leadership Monitor, September 7, 2017, https://www.aberfoylesecurity.com/?p=4010
- Blog of Mahamat Hassane Boulmaye, “Peuple tchadien meurtrie et inoffensive,” November 27, 2016, http://lepythonnews.over-blog.com/2016/11/peuple-tchadien-meurtrie-et-inoffensif.html
- UNSC: “Letter dated 5 September 2018 from the Panel of Experts on Libya established pursuant to resolution 1973 (2011) addressed to the President of the Security Council,” September 5, 2018, p.15.



