Terrorism Monitor
Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
November 20, 2025
Executive Summary:
- The Rapid Support Forces’ (RSF) capture of al-Fashir, accompanied by exterminatory extrajudicial killings after an 18-month siege, represents the militia’s most significant territorial victory to date and accelerates the effective partition of Sudan.
- With control over most of Darfur and parts of Kordofan and Blue Nile, the RSF is consolidating a parallel “Tasis State,” seeking external legitimacy despite its reliance on predatory militias and systematic abuses.
- The Sudanese Armed Forces–Transitional Sovereignty Council (SAF–TSC) coalition remains internally divided and constrained by Islamist-aligned networks, leaving both major coalitions dependent on abusive partners and limiting prospects for a negotiated national political settlement.
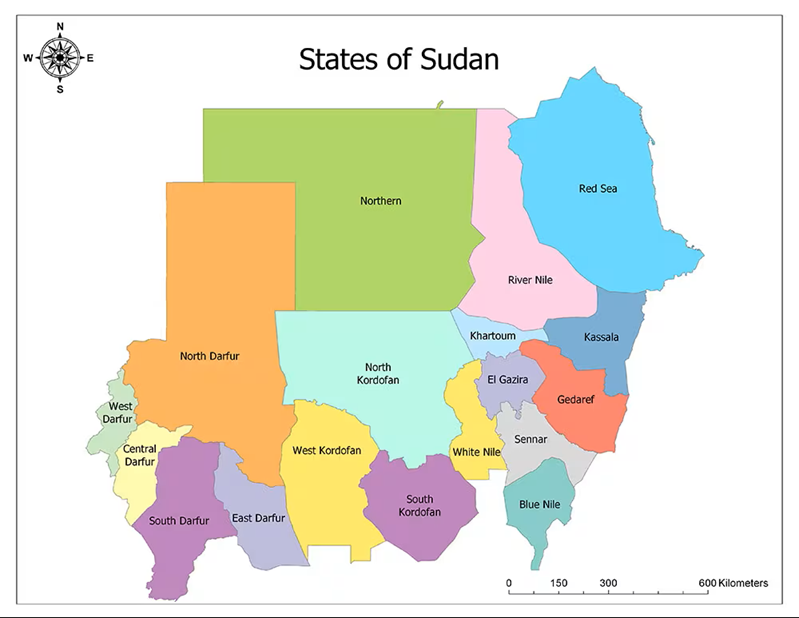
Until 2005, Sudan was Africa’s largest country by territory size. After 22 years of civil war, South Sudan separated, taking the nation’s oil wealth and roughly one-third of its territory with it. Today, after two-and-one-half years of a new civil war, the rebel Rapid Support Forces (RSF) declared its intention on July 2 to form a new state, splitting the country once again. Though the RSF’s stated intention is to form a new government for all Sudan, it is in reality now focusing on consolidating its control of the western provinces of Kordofan and Darfur, having been ejected from Khartoum and the central region of al-Jazirah by the Sudan Armed Forces (SAF) and its allies.
The initiative is designed to provide legitimacy and access to aid and arms for a paramilitary accused of genocide, ethnic cleansing, looting, destruction of cultural institutions, sexual violence, war crimes and widespread atrocities.
The Battle for al-Fashir
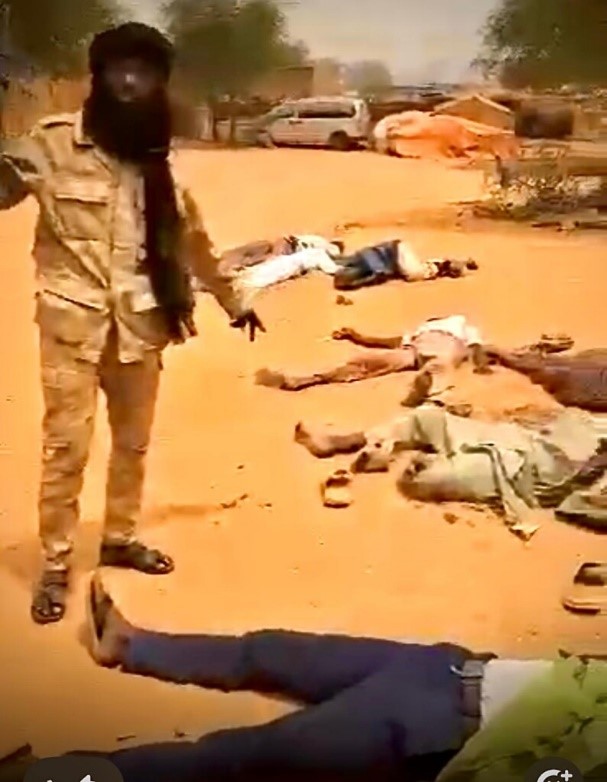 RSF Fighter with Dead Civilians
RSF Fighter with Dead Civilians
Crucial to the establishment of a new RSF state based largely in western Sudan is the seizure and occupation of al-Fashir, the traditional capital of Darfur since its founding in the late 18th century as capital of the Fur Sultanate. After an 18-month siege, the city was taken by the RSF on October 27, when the movement overran the SAF’s 6th Infantry Division and elements of the Sudan Liberation Movement-MM led by Darfur Governor Minni Arko Minawi (now resident in Port Sudan). Taking al-Fashir frees up RSF forces for the ongoing battle for neighboring Kordofan region and solidifies its control of Darfur (Mada Masr, July 11).
Minni Arko Minawi, Governor of Darfur and Leader of the SLA-MM
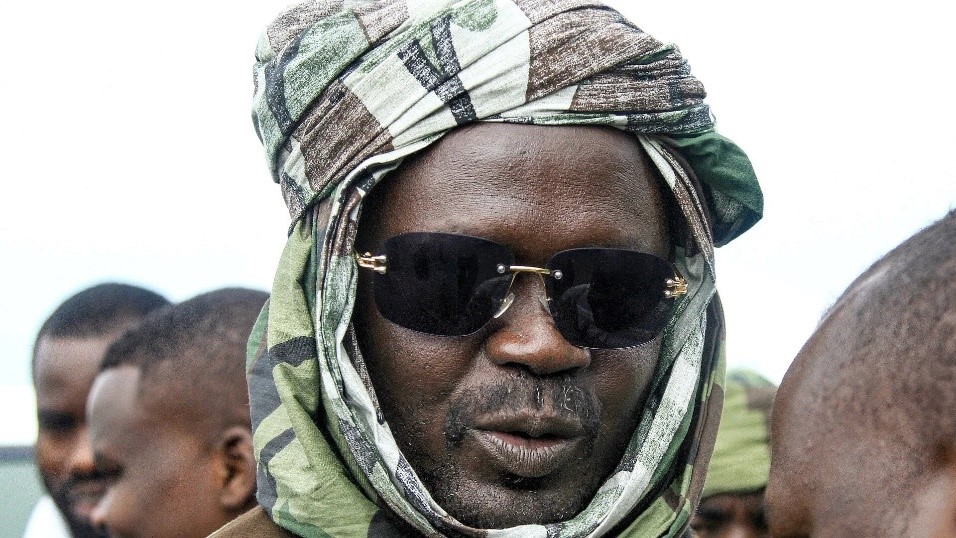
The entry of RSF forces was followed by massacres largely targeting the non-Arab population of the city that have killed at least 1500 people, including 460 patients and health workers at the Saudi Maternity Hospital (Al-Jazeera, October 30). According to the Sudan Doctors’ Network, “Hospitals in El Fasher have been transformed into human slaughterhouses” (Radio Dabanga, October 30). The atrocities appear to exceed even the dark episodes that followed the taking of al-Fashir after a siege by Mahdist forces in 1883. RSF commander Muhammad Hamdan Daglo “Hemetti” acknowledged he had “observed abuses occurring in al-Fashir” and pledged to hold RSF personnel accountable for their crimes (Sudan Tribune, October 29).
During the siege RSF constructed 68 km of 3-meter-tall sand berms alongside 3-meter-deep ditches as wide as five meters around al-Fashir to prevent escape from the siege (Radio Dabanga, September 30; Mada Masr, September 5). [1] People fleeing al-Fashir along the so-called “Road of Death” to nearby cholera-stricken Tawila were routinely deprived of all their possessions before being killed or raped as suspected supporters of the SAF. Others were forced to provide blood for wounded RSF fighters; many of these died soon after (Sudan Tribune, September 6). Those remaining in al-Fashir were reduced to eating leaves or a diminishing supply of animal feed as supplies of food, medicine and other aid were interrupted by the RSF’s siege lines (Al-Jazeera, September 4).
 Palace of Sultan ‘Ali Dinar, al-Fashir (TIKA)
Palace of Sultan ‘Ali Dinar, al-Fashir (TIKA)
Earlier this year, the RSF, having already looted the Sudan National Museum in Khartoum, bombed the historical al-Fashir palace of Fur Sultan ‘Ali Dinar (1898-1916), a revered national symbol of anti-colonial resistance, but one who campaigned constantly against the western Arab tribes that now dominate the RSF (Radio Dabanga, January 22; Darfur Network for Human Rights, January 17).
South of al-Fashir, there are indications that the RSF has turned the airbase at Nyala into a base for Iranian and Chinese-designed drones capable of striking any target within Sudan (Sudan Tribune, September 29). The RSF has also made major improvements in its air-defense systems through the use of Wagner Group-supplied surface-to-air missiles capable of downing the SAF’s Turkish-made Bayraktar Akinci high-altitude, long-endurance drones, once expected to be a game-changing weapon in the struggle to relieve al-Fashir (Military Africa, September 28).
The Tasis State
A political charter to form a parallel “transitional peace government” was signed in February by the RSF, the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement – North (SPLM-N) and other armed groups (the “Tasis Alliance”) operating in western Sudan (al-Jazeera, July 28). The new state was declared on July 26 as the “Government of Peace and Unity,” but is more commonly known as “the Tasis State.” Though the new state insists it represents all parts of Sudan, in reality it can only govern those regions currently controlled in whole or part by the RSF and the SPLM-N (Darfur, parts of Kordofan and parts of Blue Nile State). For now, the Tasis capital is in Nyala (southern Darfur), but will likely be shifted to al-Fashir.
The Tasis (“Founding”) Alliance is formed from 24 armed and civil groups, including the RSF, the SPLM-N, the Beja Congress of eastern Sudan, the Rasha’ida Arab “Free Lions” of eastern Sudan, and factions of the National Umma Party (UP), Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) and the largely Zaghawa Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) (Ash Sharq al-Awsat, March 4; Sudan Tribune, January 22). To maintain a façade of ruling all Sudan, Tasis has appointed regional governors for Khartoum and the Eastern region, despite the RSF currently having no presence in these areas (Sudan Tribune, July 26; Arab Weekly, July 28).
The head of the presidential council is RSF leader Muhammad Hamdan Daglo “Hemetti”; his deputy is SPLM-N leader ‘Abd al-Aziz Hilu (see MLM, June 2012). Both attended the swearing in of the presidential council in Nyala on August 30; the ceremony site was bombed several hours later by the SAF (Mada Masr, September 5).
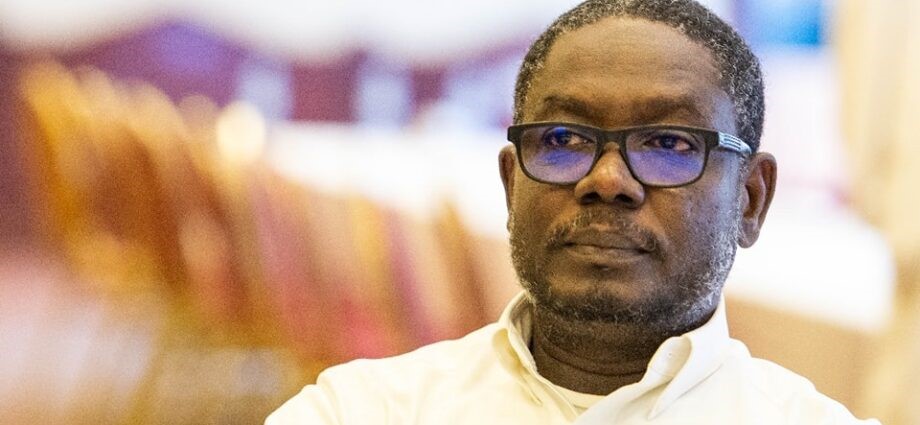 Tasis Prime Minister Muhammad Hassan al-Ta’aishi
Tasis Prime Minister Muhammad Hassan al-Ta’aishi
As prime minister, the Darfur Arabs controlling the RSF have appointed Muhammad Hassan al-Ta’aishi, a known ally of Hemetti. The appointment has significant symbolic value with reference to the rivalry between the Baqqara (cattle-herding) Arabs of Darfur and the riverain Arabs of northern Sudan in the time of the Mahdist State (1885-1898), when the northern Arab relatives of the Mahdi, the ashraf, were repressed by the Mahdi’s successor, Khalifa ‘Abd Allahi, a member of Darfur’s Ta’aisha tribe. Sudan’s northern Arab minority has dominated Sudan since independence in 1956, and the appointment of a Ta’aishi as prime minister is a political signal understood by all Sudanese.
The RSF justifies its declaration of a new state by saying it is necessitated by an urgent need for identity documents, currency, security, medicine, healthcare and education identity documents (Mada Masr, August 16). One purpose of establishing the rival state is to establish legitimacy in talks hosted by outside parties such as the Quartet – the US, UK, UAE and Saudi Arabia (better known as “the Quad”). For now, only the UAE recognizes the RSF as a de facto authority (Mada Masr, September 28). Sudan’s government has complained to the UN about the UAE’s alleged involvement in supplying arms, logistical support and Colombian mercenaries to the RSF (AIS Special Report, June 13; Mada Masr, September 14).
The UN Security Council rejected the declaration of a rival state in Sudan, calling it “a direct threat to Sudan’s territorial integrity” (UN News, August 13). It has also been opposed by many Arab states, including Algeria, Egypt, Jordan, Qatar and Saudi Arabia (New Arab, March 6). Other opposition comes from the US and the African Union (AU), which suspended Sudan’s membership in 2021. Besides the UAE, supporters include Khalifa Haftar’s eastern Libya, Chad, Kenya, South Sudan and the Central African Republic.
THE SAF/TSC Government
The Port Sudan-based SAF/Transitional Sovereignty Council (TSC) government is making its own bid for legitimacy in the face of what it regards as exclusion from international peace efforts supported by the Quad, the UN and the AU. Declaring it will not negotiate without a declaration of its legitimacy, the SAF/TSC has also rejected all efforts to place the RSF on an equal footing and insists only a military resolution can bring peace to Sudan (Mada Masr, September 20).
Finance Minister and JEM leader Dr. Jibril Ibrahim (Akhbar al-Sudan/Facebook)
On May 19, Kamil al-Tayib Idris, with doctorates in international relations and international law, was appointed Sudan’s first civilian prime minister since 2022 by General ‘Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan, head of the SAF and chair of the TSC. Shortly afterward, the new PM tried to expel two powerful former rebel leaders from the TSC cabinet, JEM’s Dr. Jibril Ibrahim (minister of finance) and Darfur governor Minni Arko Minawi, but was quickly overruled by al- Burhan, who doubtless has no desire to see these leaders and their valuable troops depart the SAF-led coalition (Al-Jazeera, July 23). Many former rebel leaders and their subordinates gained their positions as TSC ministers under the terms of the 2020 Juba peace agreement (International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance, April 21, 2021).
Traditional Parties Divided
The National Umma Party (NUP) is the political arm of Sudan’s neo-Mahdist movement and has been a strong, western-based political force in Sudan since independence under the leadership of various descendants of its founder ‘Abd al-Rahman al-Mahdi, the posthumous son of Muhammad Ahmad ibn ‘Abd Allah, “the Mahdi” (1843-1885). The party is currently divided, with a faction led by acting head Muhammad ‘Abd Allah al-Douma backing the Port Sudan SAF/TSC government while a faction led by Fadlallah Burma Nasir supports the RSF and the creation of a parallel Sudanese state (Sudan Tribune, July 8). Fadlallah has accepted an appointment to be speaker of the Tasis government’s legislative council.
 Khatmiyya Leader Muhammad ‘Uthman al-Mirghani
Khatmiyya Leader Muhammad ‘Uthman al-Mirghani
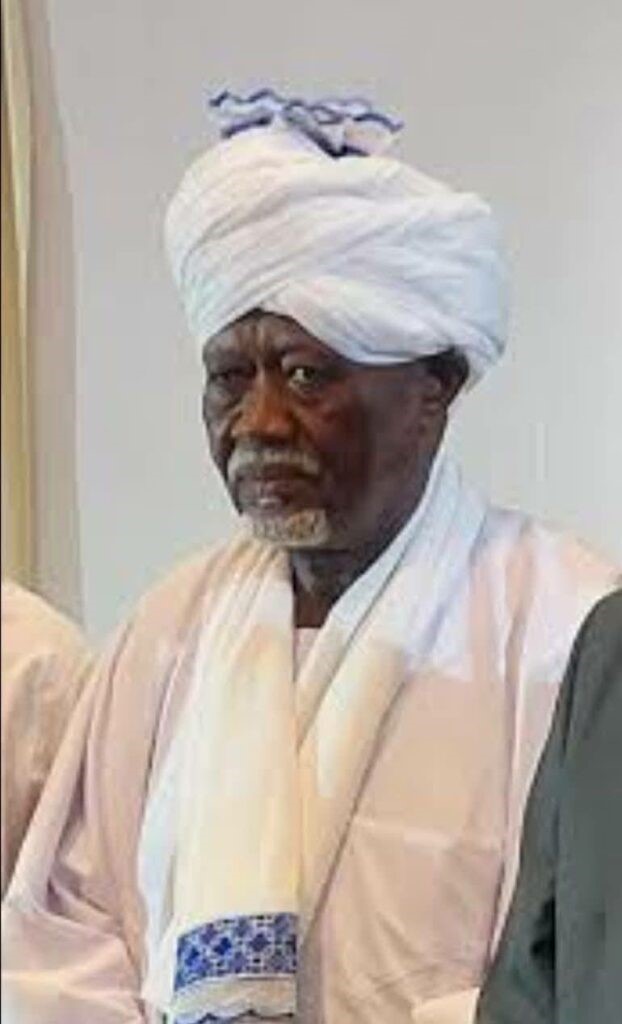
The NUP’s historical rival is the Democratic Unionist Party (DUP), led by Sayyid Muhammad ‘Uthman al-Mirghani, the 89-year-old leader of the historically pro-Egyptian Khatmiyya Sufi order and descendant of the order’s founder, ‘Ali al-Mirghani (1873-1968). The leadership of the DUP is in turmoil after decrees allegedly issued by Sayyid al-Mirghani on June 24 replaced the party leader’s son, Ja’afar al-Sadiq, as deputy leader with Ahmad Sa’ad Omar, a loyalist of deposed president Omar al-Bashir. Many DUP leaders allege the maneuver was the work of another of al-Mirghani’s sons, ‘Abd Allah al-Mahjub, who was taking advantage of the elderly Sufi leader, a resident of Cairo who is known for his publicly expressed support for the SAF but has little other political involvement (Sudan Tribune, June 25; Altaghyeer.info, July 8, 2024).
A faction under Ibrahim al-Mirghani, another descendant of Khatmiyya founder ‘Ali al-Mirghani, has come out in support of the RSF and the Tasis alliance. A DUP spokesman declared in February that “the presence of Ibrahim Ahmed Al-Mirghani does not represent the party in any way, and he only represents himself and the constituencies that entrusted him with the mission” (SUNA, February 20).
The Islamists Return
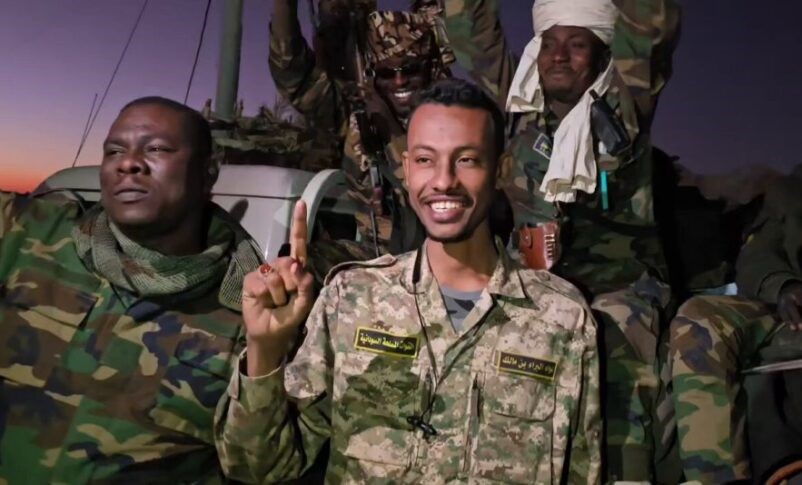
Much like the RSF-led Tasis coalition, the “official” SAF/TSC government and its armed supporters also constitute a tenuous alliance. Complicating its own search for legitimacy is the presence within the coalition of many Islamists, including veterans of the discredited military-Islamist government of Omar al-Bashir, who was deposed in 2019 and is currently wanted by the International Criminal Court (ICC) on charges of war crimes, torture and genocide. Islamist militias under SAF command have played a major role in the fighting, most notably the Bara’a bin Malik Brigade, tied to the Islamist National Congress Party (NCP).
Commander of the Bara’a Bin Malik Brigade, al-Misbah Abu Zaid Talha (Sudan Tribune)
The NCP, which ruled Sudan from 1998 to 2019, is currently led by Ahmad Harun (also wanted by the ICC on charges of war crimes and genocide in Darfur). Harun believes Western political models are inappropriate for Sudan and that there must be a political role for the army, but insists the Islamists will wait to seek power via the ballot box after the war’s conclusion (Sudan Tribune, July 25; Arab Weekly, July 26).
The RSF is strongly opposed to a political return by the Islamists, blaming them for initiating the current conflict (Sudan Tribune, July 25). Tasis prime minister Muhammad Hassan al-Ta’aishi explained in an interview that General al-Burhan has “benefited from the Islamists’ infiltration of the military establishment” and that he “became the general who served the Islamists most after the [2019] revolution” (Assayha, October 16). The Tasis alliance has declared they will dissolve all Islamist militias affiliated with the NCP after they take control of Sudan (Ash Sharq al-Awsat, March 4).
Conclusion
The problem is that there are not two groups fighting for power in Sudan, but many, who have flocked to one or the other of the major coalitions (RSF and SAF) to further their own interests, even when that has meant splitting existing movements. In turn, the leaders of the major coalitions have become beholden to unreliable partners who have a track record of opportunism. In this situation, a victory by either side may mark not the end of the conflict, but only the starting point of a new one.
Most international support (however unenthusiastic) tends to line up behind the SAF/TSC as the default successor to the line of recognized Sudanese governments. However, the civilian leaders in the TSC are in thrall to the military members of the TSC, particularly TSC chairman General al-Burhan. While many civilian members reject a return to the political Islamism of the era of President Omar al-Bashir, they must contend with the fact that the northern Arab generals of the SAF are precisely those that survived the frequent purges of non-Islamist officers during the Bashir regime.
The RSF’s new Tasis State is not without its own international support, but these backers remain focused on what can be gained by supporting a paramilitary (led by Darfur Arabs) that has adopted a veneer of statehood to cloak the fact it is manifestly incapable of running anything resembling a 21st century administration with any other objective than the personal enrichment of its leadership. The inability of both RSF and SAF commanders to envision the possibility of a Sudanese nation led by a member of Sudan’s non-Arab majority guarantees further rounds of combat focused on the pursuit of ethnic-based power sharing.
On the battlefield, ongoing atrocities by both the SAF and the RSF mean there is little to choose between them in a humanitarian sense. Beyond the deliberate destruction of national infrastructure (much of which is the now ruined and irreplaceable legacy of the brief days of oil wealth before the separation of South Sudan), a recent UN report entitled “A War of Atrocities” found both side guilty of adopting a brutal approach to achieving their attainment of power: “Both sides have deliberately targeted civilians through attacks, summary executions, arbitrary detention, torture, and inhuman treatment in detention facilities, including denial of food, sanitation, and medical care. These are not accidental tragedies but deliberate strategies amounting to war crimes” (UN Human Rights Council, September 5). Ultimately, the division of Sudan into two dysfunctional states rather than one cannot offer the Sudanese people the prospect of stability or prosperity.
Note
- “Special Report: No Safe Haven: Bombardment of Abu Shouk IDP Camp and El-Fasher’s Increasing Berm Encirclement,” September 11, 2025, https://files-profile.medicine.yale.edu/documents/e3d32307-89f9-4573-8c87-fc7d15239a9f