Andrew McGregor
July 24, 2014
With several military operations underway in the former colonies of French West Africa, Paris has decided to reorganize its deployments with an eye to providing a more mobile and coordinated military response to threats from terrorists, insurgents or other forces intent on disturbing the security of France’s African backyard.
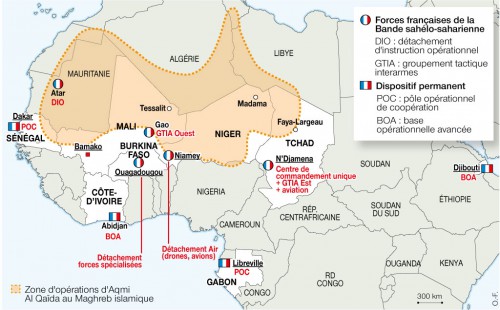
France will redeploy most of its forces in Africa as part of the new Operation Barkhane (the name refers to a sickle-shaped sand dune). Following diplomatic agreements with Chad, Mali, Niger, Burkina Faso and Mauritania (the “Sahel G-5”), over 3,000 French troops will be involved in securing the Sahel-Sahara region in cooperative operations involving G-5 troops. Other assets to be deployed in the operation include 20 helicopters, 200 armored vehicles, 200 trucks, six fighter-jets, ten transport aircraft and three drones (Le Figaro [Paris], July 13).
 President Hollande made a tour of Côte d’Ivoire, Niger and Chad between July 17 to 19 to discuss the new security arrangements with political leaders, but also to promote French trade in the face of growing Chinese competition (Economist, July 19). In Niger, Hollande was met by a group protesting French uranium mining operations in that country (AFP, July 18). In a speech given in Abidjan, French president François Hollande declared that the reorganization of French military assets in Africa would enable “quick and effective responses to crisis… Rather than having heavy and unwieldy crisis bases, we prefer to have facilities that can be used for fast and effective interventions” (Nouvel Observateur [Paris], July 19).
President Hollande made a tour of Côte d’Ivoire, Niger and Chad between July 17 to 19 to discuss the new security arrangements with political leaders, but also to promote French trade in the face of growing Chinese competition (Economist, July 19). In Niger, Hollande was met by a group protesting French uranium mining operations in that country (AFP, July 18). In a speech given in Abidjan, French president François Hollande declared that the reorganization of French military assets in Africa would enable “quick and effective responses to crisis… Rather than having heavy and unwieldy crisis bases, we prefer to have facilities that can be used for fast and effective interventions” (Nouvel Observateur [Paris], July 19).
The official launch of Operation Barkhane will come in the Chadian capital of N’Djamena on August 1. The operation will be commanded by the highly-experienced Major General Jean-Pierre Palasset, who commanded the 27e Brigade d’Infanterie de Montagne (27th Mountain Infantry Battalion, 2003-2005) before leading Operation Licorne in Côte d’Ivoire (2010-2011) and serving as commander of the Brigade La Fayette, a joint unit comprising most of the French forces serving in Afghanistan (2011-2012).
The initiation of Operation Barkhane brings an end to four existing French operations in Africa; Licorne (Côte d’Ivoire, 2002-2014), Épervier (Chad, 1986-2014), Sabre (Burkina Faso, 2012-2014) and Serval (Mali, 2013-2014). Licorne is coming to an end (though 450 French troops will remain in Abidjan as part of a logistical base for French operations) while the other operations will be folded into Operation Barkhane. Operation Sangaris (Central African Republic, 2013 – present) is classified as a humanitarian rather than counter-terrorism mission and the deployment of some 2,000 French troops will continue until the arrival of a UN force in September (Bloomberg, July 21). Some 1200 French soldiers will remain in northern Mali (Guardian [Lagos], July 15). Existing French military deployments in Djibouti, Dakar (Senegal) and Libreville (Gabon) are expected to be scaled back significantly, a process already underway in Dakar (Jeune Afrique, July 19).
 Soldiers of the 8th Regiment of Marine Infantry Paratroopers (8e RPIMa), deployed in Gabon and Côte d’Ivoire
Soldiers of the 8th Regiment of Marine Infantry Paratroopers (8e RPIMa), deployed in Gabon and Côte d’Ivoire
The force in Chad has been boosted from 950 to 1250 men. Chad will play an important role in Operation Barkhane – N’Djamena’s Kossei airbase will provide the overall command center, with two smaller bases in northern Chad at Faya Largeau and Abéché, both close to the Libyan border. Zouar, a town in the Tubu-dominate Tibesti Masif of northern Chad, has also been mentioned as a possibility (Jeune Afrique, July 19). Kossei will provide a home for three Rafale fighter-jets, Puma helicopters and a variety of transport and fuelling aircraft. Chadian troops fought side-by-side with French forces in northern Mali in 2013 and are regarded as the most effective combat partners for France in North Africa despite a recent mixed performance in the CAR. Four Chadian troops under UN command died in a June 11 suicide bombing in the northern Mali town of Aguelhok (AFP, June 11). Chadian opposition and human rights groups are dismayed by the new agreement, which appears to legitimize and even guarantee the continued rule of President Idriss Déby, who has held power since 1990 (RFI, July 19).
Intelligence operations will be headquartered in Niamey, the capital of Niger and home to French unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) operations in West Africa. There are currently about 300 French troops stationed in Niger, most of them involved in protecting, maintaining and operating two unarmed General Atomic MQ-9 Reaper drones and an older Israeli-built Harfang drone (Bloomberg, July 21). The French-operated Harfang drones are being gradually phased out in favor of the MQ-9s, though the Harfangs saw extensive service during French operations in northern Mali in 2013. Three Mirage 2000 fighter-jets will be transferred from N’Djamena to Niamey. A French Navy Dassault Atlantique 2 surveillance aircraft has been withdrawn from Niamey with the conclusion of Operation Serval.
Small groups of French Special Forces will continue to be based in Ougadougou, capital of Burkina Faso, and at Atar, a small settlement in northwestern Mauritania. Other small bases are planned for Tessalit in Mali, which controls the road running between the rebellious Kidal region and southern Algeria, and in Madama in Niger, a strategic post near the Malian border that was the site of a French colonial fort. There are reports that French troops have already occupied the nearby Salvador Pass, an important smuggling route between Niger and Libya that appears to have acted as a main transit route for terrorists passing through the region (Libération [Paris], July 16).
French forces in the Sahel-Sahara region will continue to be targeted by Mokhtar Belmokhtar’s Murabitun group, which claimed responsibility for the death of one Legionnaire and the wounding of six others in a suicide bomb attack in northern Mali on July 15 (al-Akhbar [Nouackchott], July 16; RFI, July 17). Much of the ground element for Operation Barkhane is likely to be drawn from the French Légion étrangère and the Troupes de marine, the successor to the French Colonial Infantry.
The implementation of Operation Barkhane, an apparently permanent defense agreement with five former French colonies, raises a number of important questions, not least of which is what attitude will be adopted by Algeria, the most powerful nation in the Sahara-Sahel region but one that views all French military activities there with great suspicion based on Algeria’s 132-year experience of French occupation. There is also a question of whether the new defense agreements will permit French forces in hot pursuit of terrorists to cross national borders of G-5 nations without obtaining permission first. The permanent deployments also seem to present a challenge to local democracy and sovereignty while preserving French commercial and political interests in the region. For France, Operation Barkhane will enhance French ability to fend off Chinese commercial and trade challenges and allow France to secure its energy supplies while disrupting terrorist networks and containing the threat from southern Libya.
This article first appeared in the July 24, 2014 issue of the Jamestown Foundation’s Terrorism Monitor
