Western Sahara’s Polisario Movement: Manufacturing a Threat to Global Security
Andrew McGregor
Terrorism Monitor 23(5)
Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
September 10, 2025
Executive Summary:
- Founded in 1973, the Polisario Front remains a UN-recognized secular liberation movement seeking independence from Moroccan rule. U.S. legislators are considering labeling the Sahrawi independence movement a terrorist group, fueled by allegations of ties to Iran, Hezbollah, and global jihadist networks, despite a lack of credible evidence. Accusations against the group appear to largely be intended to delegitimize the movement and reinforce Morocco’s ties with the United States and Israel.
- The recent move against the group in the West is based on claims of Iranian training, rocket attacks with Iranian weapons, and a Polisario presence in Syria that appears largely fabricated or exaggerated through Moroccan, Israeli, and Western media outlets. Credible sources and intelligence officials reject a meaningful connection.
Recent media claims have put a lightly-armed group of independence-seeking desert fighters from Western Sahara, an obscure former Spanish colony, at the heart of an Iranian-backed terrorist network with designs on Morocco, Israel, Europe, and even the United States. U.S. legislators are now preparing to designate the 52-year-old Polisario movement as an international terrorist group and a general threat to world order (U.S. House of Representatives, June 24). This would represent the culmination of a massive and often contradictory campaign of misinformation and disinformation by promoters of Moroccan interests in the region, and promote closer ties between Morocco, Israel, and the United States.
The Polisario’s Progression
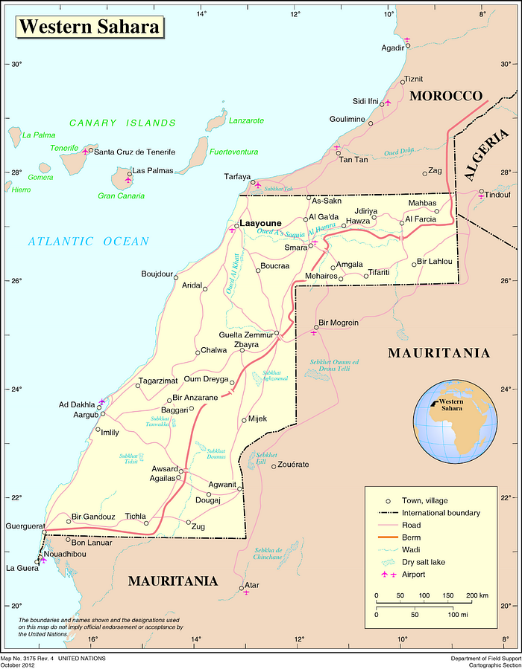
The Polisario (derived from the Spanish Frente Popular de Liberación de Saguía el Hamra y Río de Oro) was formed in 1973 with Algerian assistance to battle Spanish occupation. The Sahrawis who dwell in what is now known as Western Sahara were traditionally free-ranging nomads of Sanhaja Berber and Arab (of the Bani Hassan tribe) descent. They are Sunni Muslims of the Maliki school common to northwest Africa, and their society is tribal, with the Reguibat (who once provided native troops for the Spanish colony) forming the dominant group. The United Nations recognizes the Polisario Front as the legitimate representative of the Sahrawi people.
 As the Polisario emerged in the 1970s, it adopted the Marxist and African socialist liberation ideology favored by independence movements across the continent at the time. However, the movement abandoned Marxism at a 1991 movement congress, a move partly inspired by the collapse of the Soviet Union that year (Guardian, February 11, 1999). When Spain relinquished its Saharan colony in 1975, the Polisario Front proclaimed the independence of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic with its capital at Laayoune.
As the Polisario emerged in the 1970s, it adopted the Marxist and African socialist liberation ideology favored by independence movements across the continent at the time. However, the movement abandoned Marxism at a 1991 movement congress, a move partly inspired by the collapse of the Soviet Union that year (Guardian, February 11, 1999). When Spain relinquished its Saharan colony in 1975, the Polisario Front proclaimed the independence of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic with its capital at Laayoune.
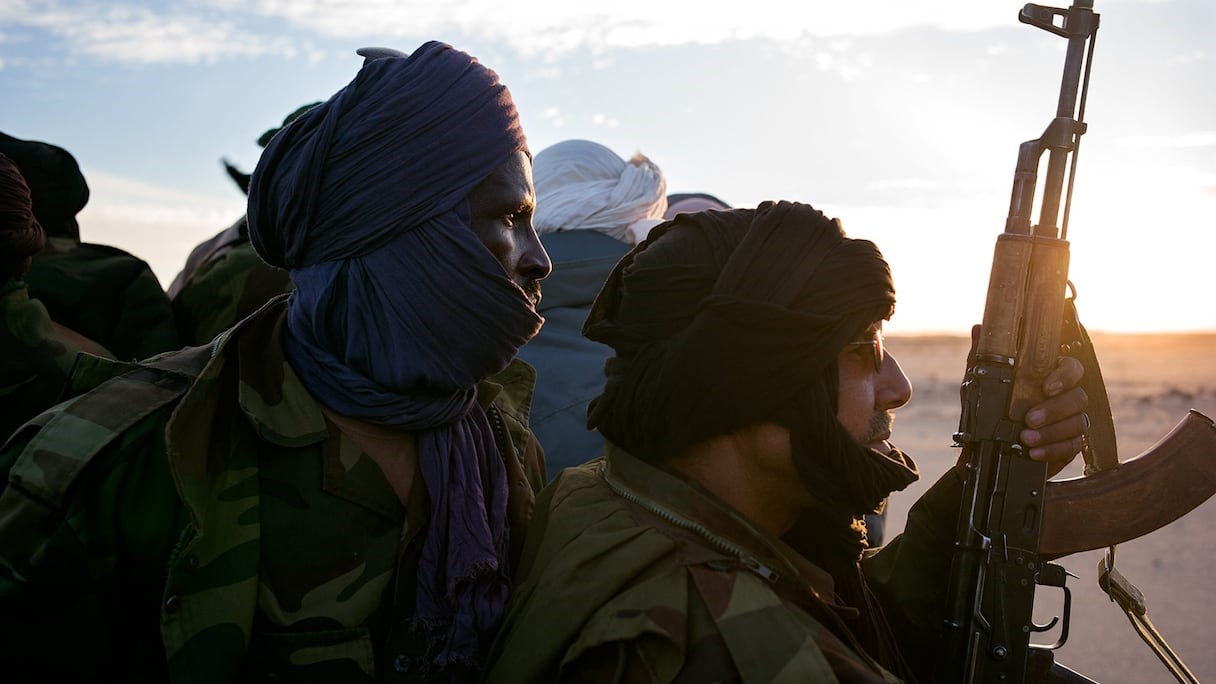
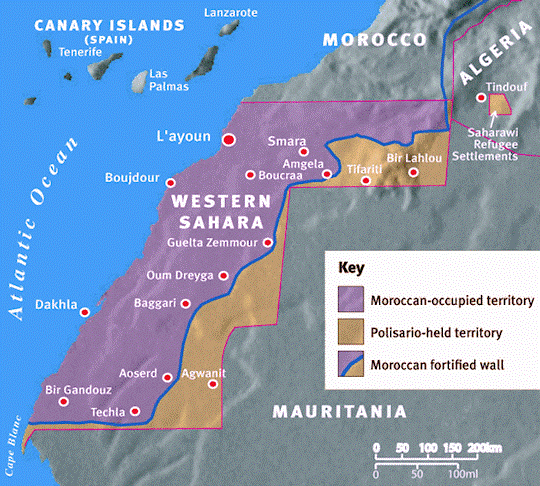
Its independence, however, was immediately challenged by both Mauritania and Morocco, igniting a 16-year war for independence that stopped after Mauritania relinquished its claims, and a ceasefire was achieved with Morocco in 1991. By this time, Morocco had taken control of 80 percent of Western Sahara, which it consolidated through the construction of a 1700-mile fortified berm (a sand wall, or “the wall of shame and humiliation” in Sahrawi parlance). Today, at least 90,000 Sahrawi refugees live across the Algerian border in camps in Tindouf, which forms the base of the Polisario and its military wing, the Sahrawi People’s Liberation Army (SPLA).
 Sahrawis in Tindouf (Dikó Betancourt)
Sahrawis in Tindouf (Dikó Betancourt)
The ceasefire has been monitored since 1991 by UN peacekeepers, the Misión de las Naciones Unidas para la Organización de un Referéndum en el Sáhara Occidental (MINURSO). The 1991 agreement called for a referendum of Sahrawis to decide on union with Morocco or independence. The referendum was never held, leaving the conflict in a state of paralysis. As disputes over voter eligibility rage on, the number of Moroccans encouraged to settle in the territory grows by the day, bringing an inevitable conclusion in favor of Rabat. Morocco has offered the Sahrawi autonomy, but is inflexible in insisting that Western Sahara should be rightfully understood as a traditional territory under the sovereignty of the Moroccan king.
In 2020, the Guerguerat incident led to the Polisario’s withdrawal from the 1991 ceasefire. Guerguerat is an important border post between Mauritania and Moroccan-occupied Western Sahara, where a Moroccan military operation against Sahrawi protesters led to clashes with Polisario fighters (Al Jazeera, November 13, 2020). The incident ignited other clashes, as the Polisario rejected the ceasefire and returned to a state of war. This unilateral move cost the Polisario badly needed international support.
Polisario’s Unwitting Entry into the Arab–Israeli Conflict
The Sahrawis have no history of engagement in hostilities against Israel. In contrast, Morocco sent a 5,500-man expeditionary force to fight alongside Arab forces in the 1973 Yom Kippur War (Jeune Afrique, November 7, 2013). Since then, Morocco, which has the Arab world’s largest Jewish population, has moved toward rehabilitating its relationship with Israel.
When Rabat signed on to the Abraham Accords (normalizing relations between Israel and Arab states) on December 10, 2020, the Trump administration rewarded Morocco by recognizing its sovereignty over Western Sahara. The idea of U.S. recognition of Moroccan sovereignty over the Western Sahara in exchange for participation in the Abraham Accords came from an Israeli group led by former Mossad deputy director and Knesset member Ram Ben Barak. The concept was then pursued by Trump senior adviser Jared Kushner and special envoy Avi Berkowitz for two years before its realization in 2020 (Axios, December 11, 2020). Morocco, Africa’s second-largest arms importer (rival Algeria is first), has in recent years turned to Israel as a major supplier of weapons, drones, and military reconnaissance satellites (The New Arab, April 16, 2024; Le Monde, May 9, 2024; Defense Post, August 15, 2024).
Since the 2020 U.S. recognition of Moroccan rule in the Western Sahara, only the Polisario has remained to be dealt with. A broad campaign emerged from sources in Israeli media, Moroccan media, and U.S. think-tanks that accused the Sahrawi separatists of jihadist terrorism and, most potently, of being willing tools of Iran’s ayatollahs. The small and once obscure movement is now alleged to be part of a “Tindouf–Tehran connection that threatens Africa’s sovereignty and security” (Atalyar [Madrid], June 2). The movement has, in addition, been accused by various groups of trafficking refugees, narcotics, and humanitarian and medical aid, as well as engaging in forced conscription and illegal detentions (Times of Israel, July 3).
The Polisario: An Iranian Proxy?
Morocco severed ties with Iran in 2018 after Moroccan foreign minister Nasser Bourita accused Algeria of providing operational support for Iranian and Hezbollah military and logistical aid to the Polisario (Al Jazeera, May 13, 2018; Morocco World News, June 30). The move helped align Morocco with the anti-Iran lobby in Washington. The Polisario, meanwhile, now faces U.S. bipartisan congressional legislation in the form of the “Polisario Front Terrorist Designation Act,” sponsored by Republican Representative Joe Wilson and Democratic Representative Jimmy Panetta, both vocal supporters of Israeli military action against Gaza and coordinated U.S.–Israeli strikes against Iran. Wilson maintains that the Polisario “is a Marxist militia” backed by Iran, Hezbollah, Cuba, and Russia, which is “providing Iran a strategic outpost in Africa” while destabilizing West Africa and the Kingdom of Morocco (X/@RepJoeWilson, January 15, June 26).
The Polisario rejects the proposed designation, in part, on the grounds that the designation requires threats to U.S. national security or U.S. citizens. The group asserts that “The Polisario Front has never attacked U.S. civilians or citizens. Its operations are directed exclusively against Moroccan military forces within the framework of a UN-recognized armed conflict” (ECSaharaui, June 27). If the legislation passes, it will make Algeria, the Polisario’s principal military, financial, and diplomatic supporter, a potential sponsor of terrorism. [1]
Alarming coverage in some British media has warned that the Polisario, “a Marxist militia backed by Iran [and] Hezbollah” (notably omitting Algeria), had plans to attack British and Israeli interests “as part of the group’s increasing terror alliance with Iran and their other proxies” (The Telegraph, July 1). Israeli sources similarly have claimed that the Polisario are “Iran-backed mercenaries operating from Algerian soil, funded by Tehran’s Quds Force, trained by Hezbollah operatives, and increasingly useful to Moscow … As Morocco deepens ties with Israel and the U.S., the Iran–Hezbollah axis sees the Western Sahara as the perfect place to retaliate…” (Ynet, April 19). The Polisario insists that “the ‘Iran–Hezbollah–Polisario axis’ narrative is entirely fabricated: a geopolitical propaganda tactic intended to associate the Polisario Front with U.S. regional adversaries, despite the lack of credible intelligence or official confirmation from U.S. security agencies” (ECSaharaui, June 27).
Shi’ite Iran’s efforts to create political and military relationships in the Sunni-majority Arab world have always been complicated by suspicion that it secretly intends to expand Shi’a religious influence. In 2022, Morocco’s foreign minister, Nasser Bourita, warned that “Iran plans to enter West Africa and to spread the Shi’a doctrine in the region” (New Arab, January 27, 2022). The Polisario, composed exclusively of Sunni Muslims, seems an unlikely tool if Iran’s involvement is religiously motivated.
The Polisario in Syria?
A document published on X by Moroccan former deputy Lahcen Haddad in December 2024 claimed that 120 Polisario fighters were sent to Syria in 2011 to receive military training from Syrians and Algerians. This was said to be done with “collaboration” from Hezbollah. The post saw wide distribution across the platform in 2025. The document offered alleged proof of the long-suspected “Iranian connection” to the Polisario. Despite claims that the file was found in “boxes of documents abandoned” by Bashar al-Assad during his December 2024 flight from Syria, it appears to have originated on a Moroccan Facebook page in April 2023 (X/Lahcenhaddad, December 10, 2024; Le360, April 21; African Digital Democracy Observatory, June 27).
Recent assertions of an armed Polisario presence in Syria include a 2024 article written by Fahad al-Masri, president of the National Salvation Front of Syria and a Paris-based Syrian expatriate dedicated to creating a Syrian–Moroccan partnership. Al-Masri claimed, based on anonymous but “reliable military sources on the ground in Syria,” that 200 Polisario fighters had been deployed by the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) to a Syrian base close to the Israeli border. There, they allegedly received Iranian training for the past three years (Ynet, November 23, 2024; African Digital Democracy Observatory, June 27).
In December 2024, the Algerian ambassador to Syria, Kamel Bouchama, made an innocent remark to the effect that some 500 Algerians or individuals of Algerian descent lived in Aleppo, Syria, including some families who had resided in the area for hundreds of years. In the hands of various Moroccan sources, the statement transformed into an assertion that 500 Polisario fighters carrying Algerian passports were under IRGC command in Aleppo. Though the ambassador clarified that the presence of these fighters was “purely imaginary,” references to the “500,” now supposedly detained and awaiting trial in Syria, continue to infect coverage of the “Iranian-controlled Polisario threat” despite no evidence of their existence (Arab Weekly, April 13; Watan News, April 25; African Digital Democracy Observatory, June 27).
The story of the “500” Iranian-trained Polisario in Syrian detention was later picked up by the Washington Post. It appeared in paragraph 30 of a lengthy piece dealing with Syrian efforts to shut down an Iranian arms smuggling route used to supply Hezbollah fighters (Washington Post, April 12). The Post article was immediately cited as U.S. “confirmation” of Iran–Algeria–Polisario connections in pan-Arab and Moroccan sources (Arab Weekly, April 13; Morocco World News, April 13).
The Post published a correction on April 24 in which the movement denied any connection with Iran. The statement offered that: “suggesting that Polisario fighters would abandon their decades-long struggle against Moroccan occupation to take part in distant conflicts is not only implausible but also an insult to the dignity and determination of a people fighting for their freedom” (Watan News, April 25). Months after the correction was published, Moroccan and Israeli sources continue to cite the Post’s report. They claim it is proof of Iran’s military training of Polisario fighters, with the Times of Israel calling it “explosive” and “irrefutable” (Morocco World News, June 11; Times of Israel, July 3).
The Attack on Smara and Potential Turn to Jihadism
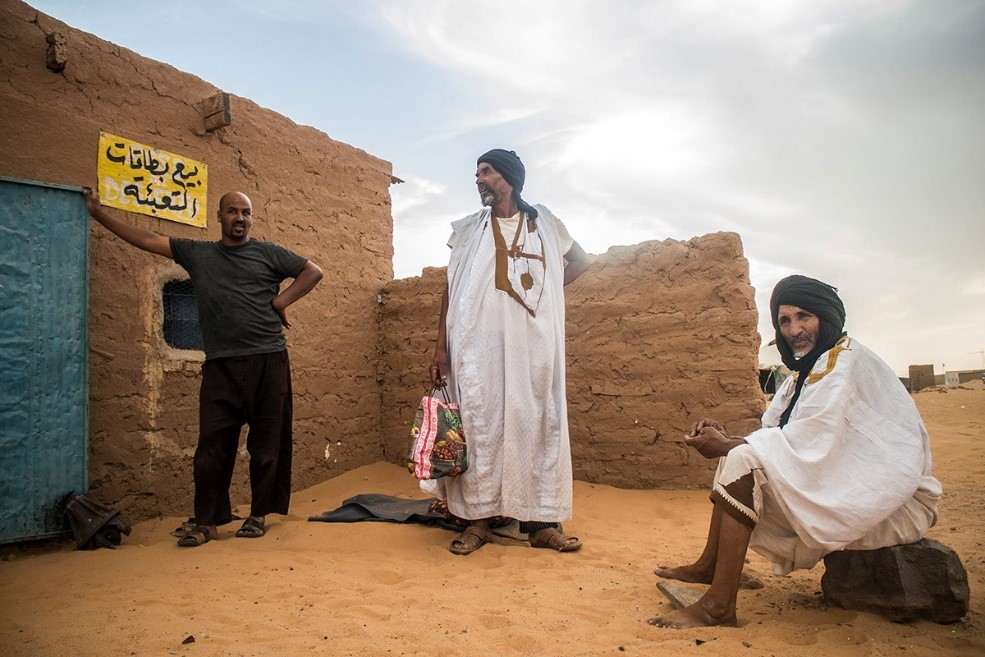
As international pressure grows, the Polisario has stepped up its still modest military operations in response. The SPLA fired four rockets at the West Saharan town of Smara (known in Spanish as Esmara) on June 27, 220 km (140 miles) east of Laayoune (El Pais [Madrid], July 2; Sahara Press Service, June 27). The Polisario claimed it had targeted “enemy military positions.” However, an inspection by MINURSO peacekeepers indicated that the rockets had hit only uninhabited areas without causing any casualties or damage (Hespress [Rabat], June 28).
 Attack on Smara – June 27, 2025
Attack on Smara – June 27, 2025
Moroccan sources reported the four rockets were Iranian-made and targeted an “educational institution” (Aldar, June 27). According to Moroccan military analyst Abderrahmane Mekkaoui, the rockets fired by the Polisario were samples of obsolete 1960s Soviet weaponry, the BM-21 122 mm Grad rocket. Mekkaoui states that the rockets came not from Iran, but from old Libyan stockpiles of the Gaddafi era, long-since seized by Algeria and passed on to the Polisario. The Polisario’s efforts to increase the range of the rockets reduced their accuracy, which Mekkaoui interprets as indicating an ideological shift to terrorism by abandoning precision guidance (in the notoriously inaccurate Grads) that could reduce civilian casualties (Hespress, June 30).
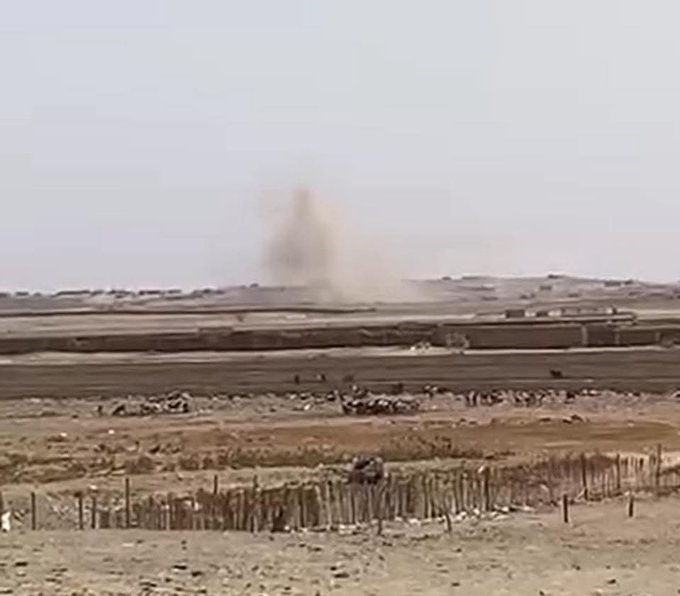
Spain’s national intelligence center (the Centro Nacional de Inteligencia, or CNI) monitors North Africa for potential threats to Spain. A recent CNI report noted that several individuals from Tindouf had acquired senior positions in Group for the Supporters of Islam and Muslims (JNIM) and Islamic State–West Africa Province (IS–WAP) (Hespress, June 8; Rue20 [Rabat], June 8; La Vanguardia [Barcelona], June 8). Most notable of these was Adnan Abu al-Walid al-Sahrawi, who spent very little time in the Polisario movement before joining a series of Salafi–Jihadi movements, ultimately becoming the leader of Islamic State–Greater Sahara (IS–GS) before his death at the hands of French forces in 2021.
 Polisario Troops Fire Rockets at Morocco, 2021 (AP/ Bernat Armangue
Polisario Troops Fire Rockets at Morocco, 2021 (AP/ Bernat Armangue
Moroccan media hailed the report as proof of the Polisario’s “involvement in terrorist activities,” with the one-time separatist movement now “an incubator of terrorism” (Rue20 [Rabat], June 11). Conversely, a CNI counter-terrorism officer who spoke recently at a Madrid conference on the jihadist threat to Spain pointed out that there were not more than 25 to 30 Sahrawis among the 2,000 to 3,000 fighters in IS–GS. While some may have attained leadership positions, it was important to note that they commanded units drawn from other peoples of the Sahelo–Sahara region. He concluded that “there is by no means a link between the Saharawi movement or the Polisario Front with jihadism” and insisted that the presence of a small number of Sahrawi fighters in IS–GS should not “stigmatize” the Sahrawi community (ECSaharaui, June 30; La Vanguardia [Barcelona], June 30). Many Sahrawis, moreover, belong to the Qadiri and Tijani Sufi orders despised by Salafi–Jihadists.
It is clear that, by joining the jihadists, this handful of Sahrawis was abandoning the secular Sahrawi independence movement rather than transitioning it into yet another group of Sunni religious extremists. To believe that the Sahrawis are Sunni Salafi–Jihadists in thrall to Iranian Shi’ite extremists (Shi’ites being a primary target of Salafi–Jihadists) is to suggest an obviously contradictory and logically impossible ideological base for the Polisario movement. If the rump Sahrawi state decided to abandon its secular ideology to become the Taliban of northwest Africa, it would meet its first opposition from the Polisario’s sole sponsor, Algeria, which fought a long and especially bitter civil war (1992–2002) against native Islamist insurgents—something Algiers has no interest in repeating.
Conclusion
The charges against the Polisario are as numerous as they are contradictory. According to its antagonists, today’s Polisario is a Marxist, jihadist, secular, separatist, terrorist, and atheist movement of Shiite and Sunni extremists and/or mercenaries trained, armed, and manipulated by the Russians, Iranians, Algerians, Cubans, Kurdish separatists, Chinese communists, and Lebanese Shiites to combat the forces of Morocco, Syrian rebels, Israel, and America. This is the cumulative result of an information war fought with greater intensity than anything the Polisario is involved with on the ground.
Evidence that Iran is supplying military equipment to the Polisario’s camps (which can only be done through Algeria) is dubious at best. Algeria, which suspected Iran of meddling in its civil war on behalf of the Islamist opposition, pursues a resolutely independent course in international affairs. It is difficult to believe Tehran would now be allowed direct access to the Sahrawi camps to arm and recruit local fighters to pursue the interests of Shiite Iran at Algeria’s expense.
Rather than posing a threat to Europe, America, the Middle East, and North Africa, the Polisario movement dwells in a perpetual state of political, diplomatic, and military weakness. The movement has never had a charismatic leader, and there is little internationally attractive about the movement’s isolated, militarized society, confined to barren refugee camps dependent on UN and Algerian aid as well as whatever else can be eked out from corruption. The alleged Polisario shift from a focus on local independence to an ambitious international agenda seems utterly perplexing, especially when it has failed to achieve any of its more modest local goals over five decades of struggle.
Note:
[1] At the time of publishing, the bill remains with the House Committee on Foreign Affairs and Committee on the Judiciary.