Andrew McGregor
February 1, 2019
Formed mostly from the tiny Zaghawa minority to which its president belongs and notorious for its corruption, the Chadian regime nonetheless presents itself to the West as an essential partner in the military struggle against Islamist extremism in the Lake Chad region and beyond. Twenty-eight years after taking power by force, Chadian President Idriss Déby Itno faces extremely difficult economic and security challenges. Chadians form one of the most impoverished populations in the world, relying on agro-pastoral pursuits for survival despite being an oil-producing nation. For nearly a decade, a once powerful but deeply divided armed opposition has been forced to operate as mercenaries and bandits in Darfur and southern Libya. However, last summer they began to make cross-border raids into northern Chad with the eventual goal of toppling the Déby regime.
 Dr. Abakar Tollimi as Secretary General of the UFDD (YouTube)
Dr. Abakar Tollimi as Secretary General of the UFDD (YouTube)
One of the most important rebel leaders is Dr. Abakar Tollimi. Unlike many of the rebel leaders, Tollimi is not a fire-breathing desert guerrilla, but rather the polished, well-mannered, French-educated face of the Chadian rebellion. Equipped with a doctorate in law, Tollimi is also distinguished locally by his lineage as part of the family of a chief of the Burogat Zaghawa clan of northern Chad (Le Point Afrique, July 17, 2017). [1] Having already played an important role in uniting and organizing the fractious Chadian opposition, it is likely that Tollimi will try to use the recent return of armed rebels to northern Chad to build a new coalition capable of tackling President Déby and the powerful Armée National Tchadienne —ANT.
 Early Life
Early Life
Abakar Tollimi was born on August 5, 1964 in the town of Fada in the Ennedi region of north-eastern Chad. After attending secondary school in the Chadian capital of N’Djamena, Tollimi graduated from Morocco’s National School of Administration and pursued further studies at the Sorbonne in Paris, where he obtained a doctorate in law in 2005.
Beginning in 1991, Tollimi spent 14 years in public administration in Chad, including work as an adviser on administrative affairs to President Déby (a Bidayat Zaghawa) (Khabar Tchad, June 3, 2016). While serving in that role in 2003, Tollimi angered the president by objecting to Déby’s planned response to the rebellion that had just broken out in neighboring Darfur. His relationship with Déby continued to deteriorate in 2006 when the president learned Tollimi was forming a political party of his own, the Popular Rally for Progress (Rassemblement Populaire Pour la Justice—RPJ). According to Tollimi, Déby warned him to “stay quiet, or I am capable of making you quiet” (Le Point Afrique, July 17, 2017). Tollimi took the advice seriously, and departed Chad the next year to join the armed opposition operating out of camps in Darfur with the connivance of the Sudanese government. According to Tollimi:
I had no intention until 2005 to take up arms. When it is no longer possible to resort to a peaceful form of struggle, when one’s own life is in danger and that one aspires to change the political life of his country, one must resort to other means… Faced with the absence of a credible civilian opposition, rebellion, the armed struggle, is the only way for possible change in Chad if we want the development of this country which is in debt in unimaginable proportions. (Afrik.com, July 7, 2010).
From the Sorbonne to the Battlefield
At a time of growing tensions between N’Djamena and Khartoum (fueled in large part by the conflict in Darfur), rebel groups formed largely from ANT deserters attacked the border town of Adré in the Ouaddaï region of Chad in December 2005. That sparked a proxy war in which N’Djamena sponsored Darfuri rebels against Khartoum while the latter sponsored Chadian rebels against N’Djamena. Tollimi’s RPJ, with its Burogat Zaghawa core, was one of the beneficiaries of Sudanese assistance. [2]
In March 2006, the RPJ was the target of a government offensive in the movement’s operational zone along the border with Sudan (BBC, March 21, 2006). The following month Tollimi was part of an attempt by the Front uni pour le changement (FUC) coalition to overthrow Déby’s regime by driving 800 kilometers from their bases near the border to attack N’Djamena. [3] The bold operation was repulsed inside the capital by government forces on April 13, 2006.
 President Idriss Déby
President Idriss Déby
The FUC signed a peace agreement with Déby’s government in December 2006 that called for the rebels to be integrated into the ANT, but many factions of the movement, including Tollimi’s, chose to remain in the field. By 2006, the FUC had joined the Union of Forces for Democracy and Development (Union des Forces pour la Démocratie et le Développement—UFDD) led by dissident general Mahamat Nouri, the former Chadian defense minister. Like General Nouri, the core of the UFDD was largely Gura’an Tubu. [4] Tollimi became the movement’s general secretary and led the UFDD delegation that helped negotiate the October 25, 2007 Libyan-hosted Sirte Accords intended to end the rebellion.
The agreement collapsed almost immediately and, in late November 2007, the UFDD fought three battles with the ANT in the Hadjer Marfain (Hyena Mountain) region of eastern Chad. The rebels were forced to withdraw through the difficult terrain with heavy losses. Angered by alleged French intelligence and logistical support to the ANT during the operation, the UFDD declared it was in “a state of belligerence” with France and “other foreign forces,” a reference to EUFOR, a European peacekeeping force that was about to be deployed in Darfur (AFP, December 2, 2007). The UFDD feared EUFOR interference with its bases along Chad’s border with Darfur. Tollimi threatened the French reconnaissance planes and helicopters he claimed were overflying UFDD positions, saying the movement would soon be “obliged to respond to this intervention” (RFI/AFP/Reuters, November 30, 2007).
On February 2, 2008, 300 pickup trucks carrying UFDD fighters arrived in N’Djamena after crossing the 800 km from their Darfur bases. Tollimi told reporters via satellite phone that the rebels controlled everything except the presidential palace, which would be stormed imminently (AFP, February 2, 2008; AFP/Reuters, February 2, 2008). This attack, like its predecessor two years earlier, was again unexpectedly repulsed at the last moment. Much of the blame was assigned to Tollimi, who failed to fully commit his forces even as the regime tottered on the precipice. Tollimi would later claim he was busy trying to act as an interlocutor with the 1,100-strong French garrison in N’Djamena, which the rebels feared might intervene on Déby’s side (Le Point Afrique, July 17, 2017). Soon after loyal ANT armored units arrived to defend the palace, the rebels were driven back into the bush in retreat. [5]
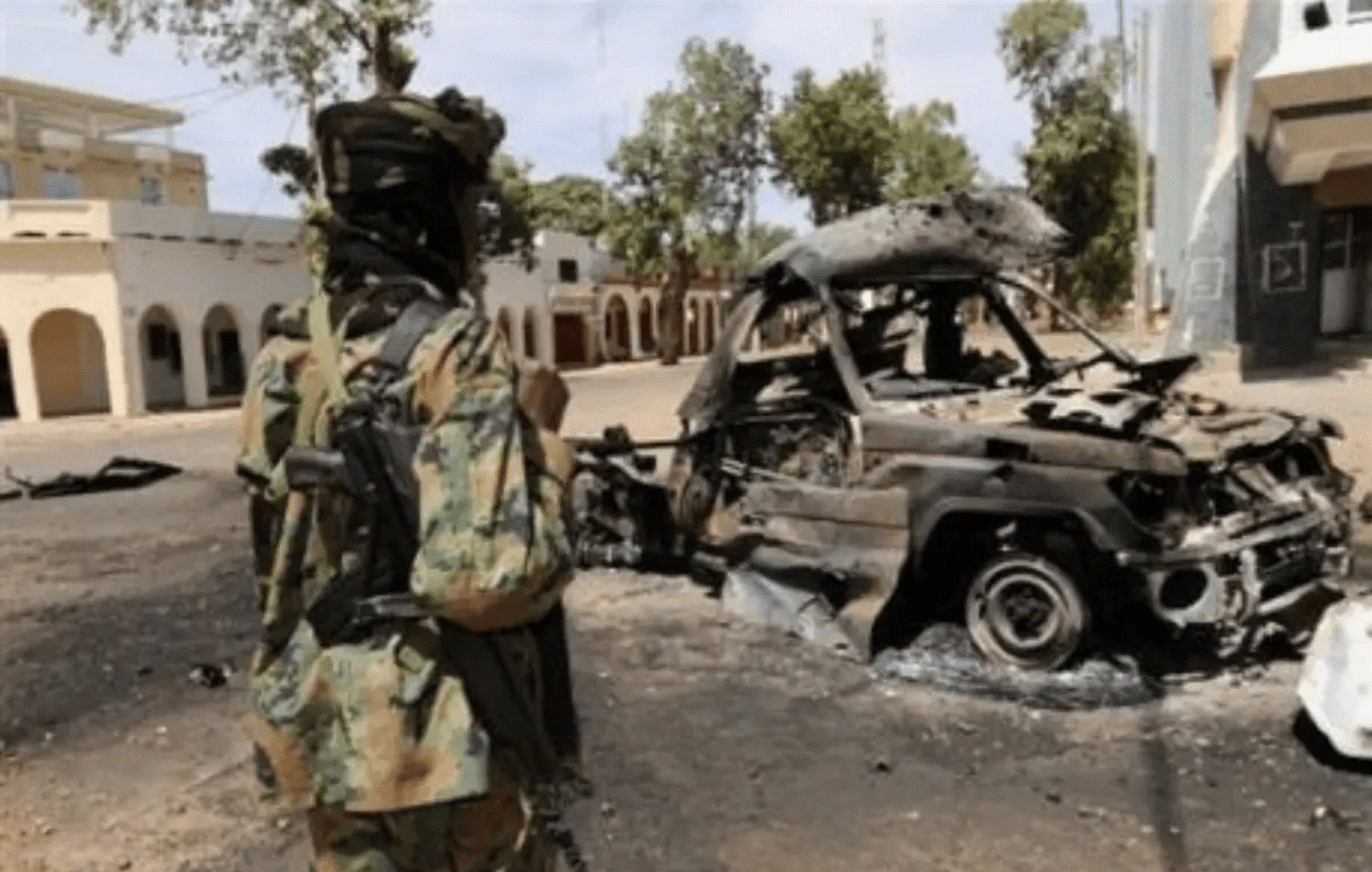 N’Djamena, 2008 (Tchadinfos.com)
N’Djamena, 2008 (Tchadinfos.com)
Afterwards, Tollimi explained his part in the attempt to overthrow the president:
I am one of those for whom the key is to put an end to the dictatorship of Idriss Déby. If we could have done it otherwise, we would have done it. Unfortunately, this man understands only the language of force. For him, everything is a balance of power and he respects only those who confront him with weapons (Tchadvision, April 2008).
Tollimi, who appears to dwell in continual political flux, became secretary general of the Union of Resistance Forces (Union des Forces de la Résistance—UFR) in 2009. An alliance of eight rebel movements based in Darfur, the UFR began operations in the Salamat region of southeastern Chad in May 2009. A series of counter-attacks by government forces failed to eliminate the movement.
Exile in France
N’Djamena and Khartoum came to an agreement to end their proxy war in early 2010, neither having benefited from it. Rebel leaders who had once been given aid and shelter were now invited to pack up their bags in both countries. As the UFR collapsed without Sudan’s support, Tollimi was deported from Sudan to France, where he was given political refugee status (RFI, July 18, 2010).
Not all was bleak, however; in 2010, a prominent French publishing house published an adaptation of Tollimi’s doctoral thesis. Entitled La Résolution des Conflits Frontaliers en Afrique (Éditions L’Harmattan), the work examines prevailing (and largely Western-based) methods of conflict resolution used in Africa while analyzing how more traditional African methods of conflict resolution could assist in solving outstanding territorial disputes, a process Tollimi refers to as “the inculturation of international law” (Afrik.com, July 7, 2010). Asked in an interview in 2008 which African politician or thinker he felt close to, Tollimi named Thabo Mbeki (president of South Africa, 1999-2008), Blaise Compaore (president of Burkina Faso, 1987-2014), Paul Kagame (president of Rwanda, 2000 to present) and, most of all, Kwame Nkrumah, “the father of pan-Africanism” (Tchadvision, April 2008).
In the meantime, Chad’s rebel movements relocated to Libya, where political chaos and rivalries provided work for mercenaries. Fighting for both of the main sides of the conflict, the rebels were able to obtain funds, arms and combat experience. Tollimi remained in France, preparing for the day the rebels might be able to return to Chad and confront Déby’s security forces. Tollimi noted at the time that the international community typically condemns armed opposition to recognized governments. This “reinforces dictatorships. The seizure of power by arms is condemned, but not the possession and maintenance of power by these same means” (Tchadenligne.com, May 5, 2011).
When the National Council of the Resistance for Democracy (Conseil Nationale de la Résistance pour la Démocratie— CNRD) was founded in March 2017, Tollimi became its president. The movement’s founding statement accused the Déby regime of establishing “nepotism, clientelism, mismanagement and state kleptomania as a system of governance” (CNRD-Tchad, March 31, 2017). The movement also made efforts to include Chadian expatriate communities in Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso) and Dakar (Senegal) (Africa Intelligence, April 19, 2017).
Declining oil prices led to protests against government austerity measures, which rocked the capital in February 2018. Déby responded by suspending 10 Chadian opposition parties while Tollimi called, unsuccessfully, for a national dialogue involving all political factions, including expatriate Chadians, civil society groups and the military (Jeune Afrique, February 16, 2018; al-Wihda [N’Djamena], March 4, 2018).
As head of the CNRD, Tollimi used an interview to criticize the Chadian government’s mismanagement of the economy and the oil revenues that never seemed to lift the greater population from poverty and despair. He said that no one in the administration could “explain what we have done with the $2 billion in revenue that the sale of oil has brought in every year… When a country does not pay the civil servants at the end of the month or closes the end of the month by resorting to loans, we are in a state of bankruptcy.” According to Tollimi, the president has deployed the Chadian military in various military interventions as a “red rag he waves to the international community” to prove his essential role in regional security efforts:
When we listen to speeches by Chad’s leaders, we gain the impression that Chad is a haven of peace, but in reality, the socio-political situation is explosive. Chad is the country with the highest risk of implosion in the sub-region and this is likely to engulf all of Central Africa if the international community and friends of Chad do nothing about it (Tchadhanana.info, March 12, 2018).
Tollimi turned down amnesty offered in May 2018, citing a continued lack of democracy (Le Monde/AFP, May 8, 2018). Recently, Tollimi has allegedly been playing a leading role in the National Front for Democracy and Justice in Chad (Front de la Nation pour la Démocratie et la Justice au Tchad—FNJDT, created in July 2018), yet another rebel coalition consisting mainly of Chadian fighters operating out of southern Libya. A video released by the new Front named Tollimi as the FNJDT chairman, though Tollimi did not confirm the appointment (TchadConvergence, July 27, 2018). The largest component of the coalition was provided by the Military Command for the Salvation of the Republic (Conseil de Commandement Militaire pour le Salut de la République —CCMSR), which was involved in battles against Chadian government forces in the Tibesti region of northern Chad from August to October 2018. [6]
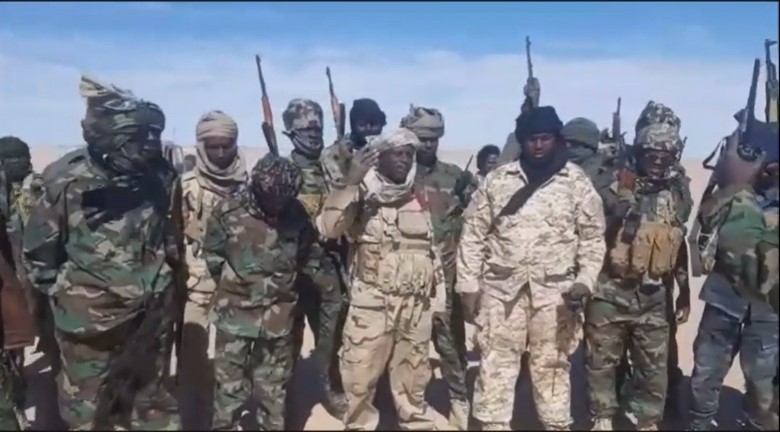

FNDJT Rebels (TchadConvergence)
On September 26, 2018, the FNJDT claimed to have surprised and captured a team of 60 Chadian Arab and Tubu commandos in Murzuk (southwestern Libya). The commandos were allegedly sent by Chad’s secret police, the National Security Agency (Agence Nationale de Sécurité —ANS), to assassinate the leaders of the various Chadian rebel movements based in Libya (al-Wihda [N’Djamena], September 29, 2018).
Tollimi and the Oil Industry
Oil production in southern Chad provides over 60 percent of the national budget, but a large proportion of these funds is lost to corruption or military spending, leaving the rest of the nation in dire poverty. Tollimi has pledged to honor commitments made by Chad in the oil sector (operated by both Western and Chinese firms), but believes a re-examination and “rectification” of certain clauses in the existing agreements is “indispensable” (Tchadvision, April 2008).
Tollimi sees a future in closer economic relations with China, possibly in an expanded role in Chad’s southern oilfields:
Beijing is the economic power of tomorrow, and China already allows us to no longer be offside on the chessboard of globalization. What African would complain? China is a partner that does not pose as a donor of lessons, and that is why it breaks with the old and hypocritical practices of some other partners (Afrik.com, July 7, 2010).
French material and political support have, despite occasional friction between Paris and N’Djamena, played a large role in maintaining the Déby regime in power. While Tollimi resents French arms deliveries to government forces and the use of French aircraft for military reconnaissance, he still maintains that a common history and cultural and economic links to France must ultimately strengthen Franco-Chadian relations, though “this must be done in a climate of neutrality and mutual respect” (Tchadvision, April 2008).
Conclusion
In early January 2019, Tollimi was one of 22 Chadians for whom Libyan arrest warrants were issued in connection to attacks on the Sidra and al-Lanuf oil terminals on Libya’s Mediterranean coast and the May 2017 Brak al-Shati attack that left 140 dead (see Terrorism Monitor, June 2, 2017). Nine Sudanese and six Libyans were also included in the warrants with Libya appealing for international assistance in apprehending these individuals (al-Wihda [N’Djamena], January 9). [7]
The CNRD protested Tollimi’s inclusion in the arrest warrants on the grounds that Tollimi had not set foot in Libya since signing the Sirte Accords in 2007 and had been conducting “peaceful political activity” in France, where the CNRD is a legal political organization (Makaila.fr, January 6). The warrants are a clear signal that legal options will now accompany the growing military pressure intended to force the Chadian rebels from Libyan soil.
Tollimi and his fellow rebels have failed to convince Paris of the necessity for regime change in Chad, resulting in reports of French intelligence and logistical support of Chadian government forces during the October and November fighting last year against the CCMSR around the Tibesti region town of Miski (Al-Wihda [N’Djamena], January 5). France and the rest of Europe are not seeking further instability along the Chad-Libya border region, part of the route taken by sub-Saharan African migrants headed for Europe.
N’Djamena hosts the military headquarters of France’s counter-terrorist Operation Barkhane, and Chad’s military plays a leading role in the battle against Boko Haram and in the French-sponsored counter-terrorist Sahel Group of Five coalition (which also includes Mali, Mauritania, Burkina Faso and Niger). Under these circumstances, Tollimi will likely find Western support for regime change in N’Djamena is minimal at present, regardless of misgivings regarding Déby’s seemingly endless rule and accusations of human rights abuses. If the regime can continue to find the funds to pay ANT salaries in a timely fashion, Tollimi may discover future attempts to overthrow Chad’s president from outside the country will be ultimately futile so long as Déby is intent on holding power.
Notes
- The Burogat Zaghawa is a Zaghawa sub-clan that resulted from intermarriage between the Gura’an Tubu and the Zaghawa.
- “They Came Here to Kill Us”: Militia Attacks and Ethnic Targeting of Civilians in Eastern Chad,” Human Rights Watch, 2007, p.69.
- In English-language literature on the movement, the FUC is often referred to by the alternate name United Front for Democratic Change (UFDC).
- “Alliance nationale pour le changement démocratique/ National Alliance for Democratic Change (ANCD),” Small Arms Survey, Geneva, March 2011, http://www.smallarmssurveysudan.org/fileadmin/docs/archive/other/armed-groups/HSBA-Armed-Groups-ANCD-March-2011.pdf
- See “Dr Abakar Tollimi SG UFDD à la tête de colonne1,” YouTube, March 21, 2008, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AVMhyDpl0mE
- See “War in the Tibesti Mountains – Libyan Based Rebels Return to Chad,” AIS Special Report, November 12, 2018, https://www.aberfoylesecurity.com/?p=4308
- Other Chadian rebels cited in the warrants for mercenary offenses, murders and kidnappings in Libya include Mahamat Nouri, Ali Ahmat Abdallah, Adoum Hissein, Hassan Hissein, Timan Erdimi, Hassan Bouloumaye, Ali Oumar, Michelet Detapol, Mahamat Hakimi, Hamid Djorou Margui, Hassan Moussa Kelley, Mahamat Moussa Margui, Mahamat Mahdi Ali and Bichara Hadjar Erdi.
 Photos of alleged Russian mercenaries in Khartoum (The Times)
Photos of alleged Russian mercenaries in Khartoum (The Times)






