Terrorism Monitor 21(22)
Jamestown Foundation, Washington DC
Dr. Andrew McGregor
November 17, 2023
 Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant (All Israel News)
Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant (All Israel News)
The deadly October 7 Hamas operation was designed to use shock and terror to force a change in the status and future of Gaza’s Palestinian population. In this regard, the operation has been successful—life in Gaza will never be the same. According to Israeli authorities, part of these changes will include the disappearance of Hamas as a political and military entity. During a meeting at the Israeli Air Force operations headquarters, Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant said of the planned Israeli Defense Force (IDF) land offensive into Gaza: “This has to be the last maneuver in Gaza, for the simple reason that after it, there will not be a Hamas” (Arutz Sheva, [Beit El] October 22). National Security Council chief Tzachi Hanegbi has pledged Israel will “wipe [Hamas] from the face of the earth” (Times of Israel, October 14).
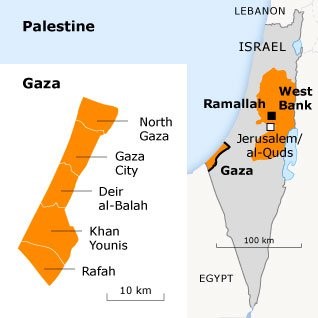
What then will a post-Hamas Gaza look like if the IDF succeeds? To follow are eight possible directions for Gaza’s future, which may involve one or more of these scenarios in combination:
Scenario 1: Return of the Palestinian Authority
After Hamas’s violent expulsion of Fatah from Gaza in 2007 and the subsequent dissolution of the Palestinian Unity government, Gaza and the West Bank have had little official interaction. This means the Palestinian Authority (PA) government in the West Bank (dominated by the Fatah Party of President Mahmud Abbas) has little presence or influence in isolated Gaza.
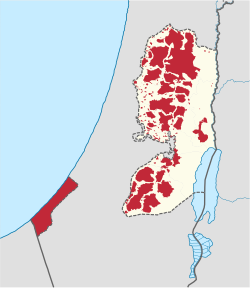 Shrinking Palestinian Territories in red, including Gaza and parts of the occupied West Bank.
Shrinking Palestinian Territories in red, including Gaza and parts of the occupied West Bank.
The credibility of the PA, should it return to Gaza, could only suffer by following behind Israeli troops, unless some sort of intermediate administration was established. Even afterwards, it would be difficult to avoid being characterized as Israel’s puppet. If Gazans are allowed to remain, Israel will certainly intensify rather than relax its control of the enclave, which will be sealed even tighter to prevent the supply of money or weapons to any resistance factions in Gaza. Moreover, the PA may not be eager to rush back into Gaza, especially if it remains politically unsettled.
Scenario 2: Islamist Extremist Groups Grow in Influence
Israel’s plan to destroy Hamas (and presumably the Gaza-based Palestinian Islamic Jihad movement and other minor Islamist militias) will leave a dangerous power vacuum in an already deeply traumatized region. This void is unlikely to be filled by any group or movement sympathetic to Israel. Palestinian anger may well encourage the growth of greater extremism. This could possibly manifest itself in new forms or in the rise in popularity in Gaza of more familiar groups, vis-à-vis al-Qaeda or Islamic State.
Scenario 3: Israeli Occupation
If, as expected, the IDF occupies all of Gaza, it will be the third such operation since the 2005 evacuation of Israeli troops and settlers. Returning Gaza to Israeli military occupation 18 years after disengagement is an idea with virtually no support in Israel or anywhere else. Israel is eager to escape an attack-response cycle that is expensive in economic terms, militarily demanding, and politically damaging.
Scenario 4: Return to Egyptian Control
Currently, Egypt has as little to do with Gaza as is possible and frequently closes its single border crossing with the enclave. Despite this, Egypt has a long history of being the dominant power in Gaza, going back as far as Pharaonic times, through the Muslim Ayyubid dynasty to the era of the medieval Mamluks before it passed into Ottoman control in the 16th century. Gaza was absorbed into Gamal Abd al-Nasser’s United Arab Republic (UAR) in 1959, and was ruled by an Egyptian governor until 1967. Before then, Egypt held Gaza with the Egyptian Army’s 8th Division, which was formed from Palestinian conscripts and Egyptian officers. Israel seized Gaza and Sinai from Egypt in the 1967 Six-Day War. While the Sinai Peninsula was eventually returned to Egypt, Gaza was not, and it remained under Israeli military occupation until 2005.
 The Rafah Border Crossing between Gaza and Egypt
The Rafah Border Crossing between Gaza and Egypt
Officially, Egypt continues to advocate for an independent Palestinian state based on the borders that existed prior to the June 1967 Arab-Israeli War. Pro-Palestinian rallies have been organized under the aegis of President al-Sisi’s Mustaqbal Watan (Future of the Homeland) party and directed by officials believed to be undercover police. Unsanctioned protests of support in Cairo’s Tahrir Square and at al-Azhar mosque, however, have been met with beatings and mass arrests (MENA [Cairo], October 23; Al Jazeera, October 21). It is clear that Egypt’s response to the war in Gaza will be formed in government meeting rooms, not on the street.
Hamas can expect no help from Egypt, because of the group’s close connections to Egypt’s banned Muslim Brotherhood. In Cairo’s view, many Gazans are infected with Islamic extremist ideology, and are suspected of collaborating with Islamist fighters in the Sinai who continue to be engaged in a 12-year-old insurgency. Egypt already hosts 9 million refugees, mostly from Middle Eastern or African countries. There is no desire in Cairo to resume Egypt’s historical control of Gaza or its 2.2 million people. Such an occupation would bring Egypt into direct contact with Israeli security forces in an unstable tinderbox. Five decades of peace with Israel have benefited Egypt, which contends with many other challenges that will not be improved by confrontations with the state. Nonetheless, as a major leader of the Arab world, President al-Sisi asserts that in Gaza “the existing reaction exceeds the right of self-defense on the part of Israel, and is turning into collective punishment” (al-Hurra [Cairo], October 16).
Cairo is also concerned that the Gaza conflict is taking international attention away from the still-raging conflict in neighboring Sudan (Ahram [Cairo], October 22; see TM, April 28). Nine thousand people have been killed in Sudan since April, while Egypt has reluctantly received over 300,000 Sudanese refugees. Cairo is hard-pressed to handle refugee pressures on both its southern and northern borders and is looking for greater international intervention to bring an end to the six-month old war in Sudan.
Scenario 5: Depopulation of Gaza
Israel is using a combination of airstrikes and warnings to compel Gazans to move to the southern part of the enclave, close to the Egyptian border. This has led to fears that Israel may seek to drive the entire population of Gaza across the border into Egyptian Sinai. Consistent with this, on October 18, President al-Sisi remarked that beyond Israel’s “direct military action” against Hamas, there was “an attempt to push the civilian population to seek refuge” in Egypt (Daily News Egypt, October 18). In a meeting with the British PM, al-Sisi declared: “We must not allow a civilian exodus from Gaza to Sinai because it would be a very dangerous matter…” The Egyptian president further warned that the consequences of failing to contain a growing spiral of violence “go beyond the right to defend oneself” (Ahram Online [Cairo], October 20). Desperate to avoid this wave of Gazan refugees, al-Sisi suggested they could instead be funnelled into Israel’s sparsely populated Negev Desert (Egypt Independent, October 18; Middle East Monitor, October 19).
Western suggestions that Egypt take in over a million Gazan refugees have angered the Egyptian government, with one senior official reportedly telling a European envoy: “You want us to take one million people? Well, I am going to send them to Europe. You care about human rights so much—well, you take them” (Middle East Monitor, October 19).
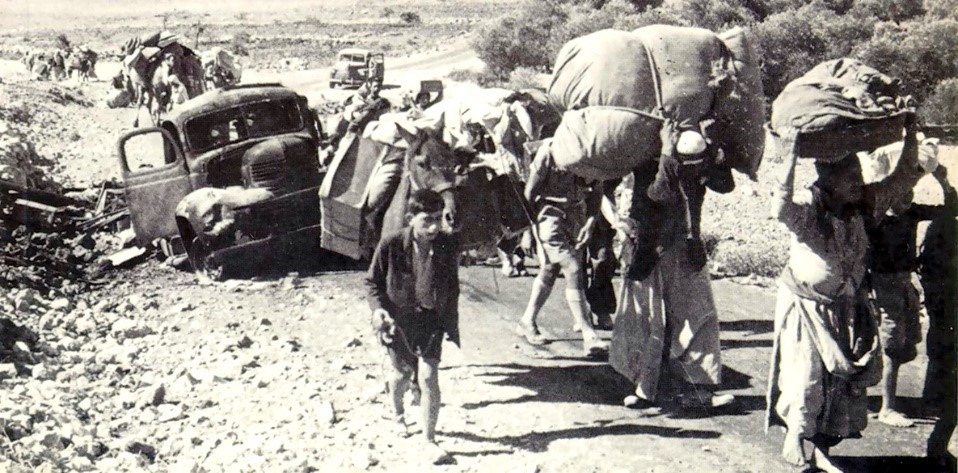
PA leader Mahmud Abbas also fears the permanent displacement of the Gazans, suggesting this would constitute “a second Nakba,” referring to the 1948 expulsion of some 750,000 Palestinians from lands that would form the state of Israel (Al Jazeera, October 13). Ariel Kallner, a Knesset member from Israel’s ruling Likud Party, issued a call for another expulsion: “Right now, one goal: Nakba! A Nakba that will overshadow the Nakba of 48!” (al-Arabiya, October 8). Another Likud member, Revital Gotliv, has called for the use of nuclear weapons to destroy Gaza and render it uninhabitable: “It’s time to kiss doomsday!” (Middle East Eye, October 22; Middle East Monitor, October 10). These remarks were echoed by Heritage Minister Amichai Eliyahu of the Otzma Yehudit Party (a Likud coalition partner), who suggested that a nuclear strike on Gaza was “one of the options” (though he later claimed he was speaking “metaphorically”) (Jerusalem Post, November 6). He further suggested that Gazans could “go to Ireland” (Dublin has been critical of the Israeli offensive in Gaza) (Times of Israel, November 5). Such calls for the depopulation of Gaza and the permanent dislocation of its people do not encourage evacuation from targeted areas nor cooperation with the IDF. [1]
 Ariel Kallner (Times of Israel)
Ariel Kallner (Times of Israel)
A leaked document from Israel’s Intelligence Ministry (described as a “concept paper”) suggested “large-scale migration from war zones … is a natural and sought-after outcome…” Among the countries mentioned as possible destinations for a mass exodus of Gazans are Greece, Spain, and Canada. The latter is singled out as a prime choice due to its “permissive immigration policy” (+972 Magazine [Tel Aviv], October 30).
Scenario 6: Establishment of a UN Mandate
One possible direction for a post-Hamas Gaza involves the revival of mandated territories, such as were common in the Middle East and Africa in the interval between the first and second world wars. Gaza itself was under the British Mandate for Palestine from 1923 to 1948. Under the auspices of the League of Nations, these mandates typically involved the transfer of former European colonies or parts of the Ottoman Empire to the control of other European nations with an eye toward guiding these territories into a state of self-determination and independence. In practice, the mandates simply maintained colonial status under new masters who were in no hurry to establish self-governance.
Assuming such a mandate is approved by the UN Security Council, which is not necessarily likely, a return of Gaza to European control under a UN mandate is simply a non-starter. Broad international participation would be required, including a massive operation involving peacekeepers, reconstruction assistance, medical and development aid, and infrastructure repair. It would be difficult to secure support for such a program from all the badly-divided members of the permanent UN Security Council. With the UN already overstretched and underfunded (especially with regard to humanitarian aid), approval of a UN mandate would only be the first step in a long and difficult process. Yisrael Beitenu Party leader Avigdor Liberman (a former defense minister, foreign minister, and deputy prime minister) has suggested that the UN forgo providing any aid to Gaza in favor of sending assistance to Libya, Sudan, and Syria instead (Jerusalem Post, October 18).
Scenario 7: Arab League Occupation
It has been suggested that some Arab nations friendly to Israel (specifically Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates) could be handed a mandate over a disarmed Gaza (Israel Hayom, October 16). Israel would determine “how the international force can operate, what weapons it is allowed to have, and anything else that effects the Jewish state’s security needs,” effectively making such a force little more than an Israeli proxy (Israel Hayom, October 19). However, there is no lineup of Arab nations ready and willing to assume responsibility for struggling Gazans living in ruins.
Some of these formerly friendly Arab states may also be growing less friendly by the day. For example, nine nations, including at least seven that might be called friendly to Israel, issued a statement on October 26 assailing Israel’s conduct of the conflict: “The right to self-defense by the United Nations Charter does not justify blatant violations of humanitarian and international law.” They further rejected any attempt “to displace the Palestinian people from their land in any way, considering it a serious violation of international humanitarian law and tantamount to a war crime” (Asharq al-Awsat, October 26). [2] The Arab League, which has no joint military mechanism, has not yet expressed any interest in assuming control of Gaza.
Scenario 8: Survival/Revival of Hamas
In a policy born of anger rather than feasibility, Israel has set itself the impossible task of eliminating every trace of Hamas, which has both political and armed wings. Short of killing or expelling every resident of Gaza, this will prove impossible. Part of the problem is the success Hamas has had in eliminating internal threats to its rule, leaving Gazans with few political alternatives. With deep roots in Gaza, there is a strong chance that Hamas will survive the current round of fighting, even if it does so in a slightly different form or under a different name.
Conclusion
Israel has regarded Gaza as an independent Palestinian state since its withdrawal in 2005 and is thus likely to repudiate responsibility for the territory when military operations are complete. As two veteran Israeli intelligence authorities recently stated: “It needs to be clear that neither Gaza reconstruction nor care for the health, sanitation, or displacement of residents is Israel’s responsibility” (Times of Israel, October 21). Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant likewise insists that the final phase of Israel’s ongoing assault on Gaza will involve “the removal of Israel’s responsibility for day-to-day life in the Gaza Strip” (Times of Israel, October 20).
There will inevitably be calls from so-called “progressive” factions in the West to allow mass migration of Gazans to Western nations, which could receive support from some Israeli leaders anxious to be done with the Palestinians. There are, however, already demands from Republican presidential hopefuls and others to ban Palestinian entry to the United States (Times of Israel, October 19).
With so many variables in play, one thing about the future of Gaza is still clear—the people who will not have a say in it are the Gazan people themselves.
Notes:
[1] Israeli government documents from 1948 were declassified in 2021 and confirm long-standing reports of massacres and forcible evictions, as well as the shocked responses of some Israeli cabinet members to the violence. The documents were examined in a report by Israeli daily Haaretz and the Akevot Institute for Israeli-Palestinian Conflict Research entitled “Classified Docs Reveal Massacres of Palestinians in ’48 – and What Israeli Leaders Knew” (Haaretz, December 9, 2021).
[2] The document was signed by the foreign ministers of Egypt, Jordan, Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait, and Morocco.