Dr. Andrew McGregor
November 8, 2007
In the far north of Scotland the Highland mountains grow smaller, eventually leveling out into vast stretches of rolling countryside that end abruptly with rocky cliffs lurching out over the cold northern seas. Before the Celts arrived these lands were ruled by Norsemen, the powerful ‘Sea-Kings of Orkney’. The names of their settlements in Scotland’s northeast county of Caithness reflected their beliefs, like the town of Thurso, named for the Norse god Thor.
 Northern Scotland
Northern Scotland
Though the town still stands after all these centuries, it came perilously close to obliteration one day in 1649. That year’s raid on Thurso by a small group of veteran Irish fighters and a handful of Scottish highlanders is not found on any list of Scotland’s great battles, but the raid was significant largely for one reason – it marked the last gasp of the once powerful Irish brigade (known as ‘Redshanks’) that came to Scotland to aid the Marquis of Montrose and his Royalist forces during the British Civil War.
Combining innovative tactics with somewhat antiquated weapons the Irish won a resounding series of victories for a year after their arrival in Scotland in 1644. Warfare in Britain was in transition during the 17th century. Pikes and muskets dominated the battlefield but there was still a place for men like the Irish who were expert in the use of sword and shield. The matchlock musket was difficult and time-consuming to load and could only be used effectively in battle by highly disciplined troops performing a complicated drill.
In battle the musketeers commonly formed up in six ranks. After the front rank fired in volley they would ‘countermarch’ to the rear to begin reloading while the next rank moved to the front to fire their volley. Inexperienced troops found the maneuver difficult. Nervousness interfered with the dozens of steps involved in reloading the musket, while the men in the front rank tended to discharge their weapons quickly and without aim in order to take their place at the rear again as soon as possible. Many Civil War battles were lost because half-trained musketeers would have been more useful with pikes in their hands rather than firearms. Artillery was often present on the battlefield, but tended to be so poorly served that it had little impact. Unlike the romantic image of charge and counter-charge by valiant swordsmen against resolute defenders, many Scottish battles of the era degenerated into rock-throwing by both sides.
The trained swordsmen of the highland clans had a fearsome reputation, but in reality they were always few in number. Most of the clansmen formed an untrained rabble, useful only for pressing home an advantage already won by the professionals in the first rank. In the impoverished Highlands there were few who could afford the expensive tools of a Celtic warrior – a broadsword, a targe (shield), a dirk (short-sword), a musket and pistols. Each clan maintained a small group of professional fighters who kept close to the chief and led the rest of the clan into battle. Most of the barefoot men brought on campaign had to wait for someone to be killed in order to seize a weapon for themselves. Nevertheless, the highlanders achieved several notable victories serving under Montrose, but their desire to return home immediately with their loot resulted in an unfortunate tendency for the highland ranks to dissolve after a victory as surely as if they had been defeated.
In the end the total numbers brought to the battlefield mattered far less than the number of professional soldiers involved on each side. A small core of men skilled in the use of their weapons and tempered in the continental battlefields of the Thirty Years War could easily rout far larger numbers of inexperienced men. It was in this sense that the largely veteran Irish Brigade (which may have included many MacDonalds from the Western Isles) was able to have an immediate impact in the Scottish campaigns of the Civil War. Under their leader Alistair MacColla (sometimes known as ‘Colkitto’), the Irish perfected a tactic that came to be known as ‘the Highland Charge’ after its adoption by Scottish highlanders. The tactic involved getting in close to the enemy before letting off a single short-range volley from their muskets into the front ranks. The muskets were then tossed aside as the Irish and their highland allies took sword in hand to emerge screaming from the smoke of their musket-fire. With the hard-charging Celts bearing down fast only seasoned regulars could be expected to resist the urge to break and run at this point. Just as important to Montrose as the fearsome reputation of his Irish fighters was their discipline under fire and their willingness to fight defensive actions as well as charge headlong into the enemy. Between battles the brigade remained an organized, armed force while the highlanders came and went according to their needs and whims. To be fair, most of the highlanders had farms to tend to, animals to care for and families who were unlikely to survive long without male providers and defenders. Any booty that could be obtained through battle was desperately needed at home.
In mid-1646 Charles surrendered to the Scottish army campaigning in England. In a bizarre turn of events the King now made an alliance with his bitter foes, the Scottish Covenanters (so-named for their ‘national covenant’ against the King’s attempts to interfere with Scottish Protestantism). The latter insisted the King disband his forces. Many of the surviving Irish fighters in Scotland began to return home in small groups or joined up with armed groups in the Western Isles and Highlands. Alistair MacColla refused to lay down his arms but was soon bottled up in Kintyre with a group of Irish and highlanders (mostly MacDonalds) by the pro-government Campbells. MacColla was driven out the next spring, fleeing to Islay Island and eventually to Ireland. By February 1647 the Covenanters had tired of the King’s prevarications in fulfilling their demands. Charles was turned over to the English Parliamentarians and the Scottish army returned home, ready to mop up the last Royalist resistance. Isolated castles and their Royalist garrisons fell one by one. Captured highlanders were typically paroled, but the Irish were almost always massacred, sometimes by the hundreds. It quickly became routine to hang any Irishman captured in Scotland, encouraging those Irish Redshanks still at large to make their way back to Ireland. Many Catholic highlanders joined them to continue the fight in Ireland, but these groups were soon destroyed in a pair of disastrous battles.
On January 30, 1649, Charles I was executed by the Parliamentarians in London. By this time there were few Irish fighters left in Scotland. Those who remained at first fought on as bands of guerrilla fighters, but they eventually developed a taste for looting, robbery and extortion. One of these bands was led by Donald Macallister Mullich, a “powerful and ferocious” Irishman who fought under Montrose in the Civil War. The band’s activities gained notice after they became involved in a spectacular robbery with Niel MacKay, leader of the Abrach MacKays in Strathnaver (please note, “Niel” is not a misspelling).
In 1648 the Earl of Sutherland sent a large armed party under his chamberlain to collect the rents in Strathnaver. Niel MacKay disputed the Earl’s right to collect rents in parts of Strathnaver and was prepared to enforce his point of view with the sword. MacKay persuaded Donald Macallister’s band of a dozen Irishmen to help him; together they drove off the taxmen and relieved Sutherland’s chamberlain of all the rents he had already collected. The Earl went to Edinburgh to complain before Parliament personally, obtaining there a company of 100 soldiers to help bring Niel MacKay to justice. The government men could not find the fugitive in the forest, nor could they find the cave that became his temporary home. The latter was described by 19th century author Robert MacKay as being “in the side of a mountain, scarcely perceptible, and so narrow at the entry as only to admit of one on all fours, but so roomy within as to contain a great number of men, and admitting air at the top through a cranny in the rock.”
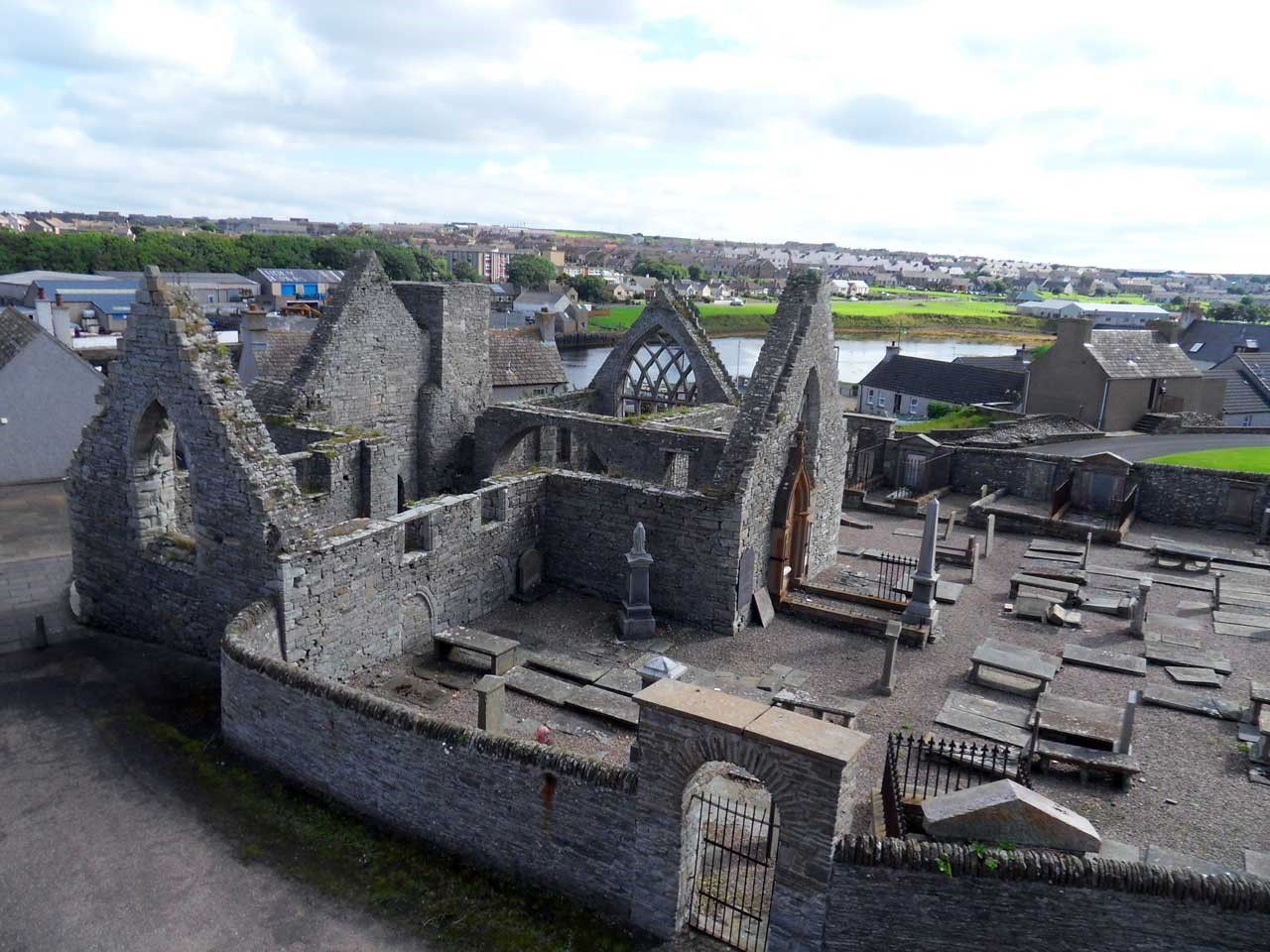 Old St. Peter’s Church (Caithness.org)
Old St. Peter’s Church (Caithness.org)
A year after the robbery Niel MacKay arrived in Thurso to visit Sir James Sinclair of Murkle. He seems to have been followed there by Macallister, who had added several Highland desperadoes to his band of hell-raisers. As was his habit wherever he went, Macallister sent a message the civic leaders of Thurso demanding coin and provisions. Outraged by their refusal, the Irish captain decided to help himself by raiding the town on a Sunday when everyone would be in St.Peter’s church. Macallister was also determined to wreak his revenge for the townspeople’s defiance by torching the church during services. When one of his ruffians objected to such blasphemy, Macallister replied in bold Gaelic; “In defiance of God and the Sunday, Donald will spill blood”.
At the time, MacKay was living with a handful of retainers in a house at a fair distance from Thurso. When the locals learned of Macallister’s arrival outside the church, they armed themselves and led by Sir James Sinclair (who habitually took his sword to church) they attacked the bandits. Driven from Thurso, Macallister headed to MacKay’s house with the enraged citizens close behind him.Despite being close friends with the Irishman, MacKay may have been unaware of Macallister’s plans for Thurso and was certainly unprepared for battle with only a small group of men at hand. The arrival at MacKay’s home of his recent ally Macallister and his raiding party was enough to convince the people of Thurso of MacKay’s connivance in a scheme to pillage the town and murder its people. It was not long before MacKay and his men were fighting side-by-side with Macallister’s bandits.
The fight was bitter and relentless, with the caterans defending the house falling one by one to the furious attackers. Having survived countless battles, there was a common belief that a lead bullet could not kill the Irish marauder Macallister. One of Sir James Sinclair’s servants cut a silver button from his master’s coat and loaded it into a pistol. Determined to slay Macallister, the would-be killer succeeded only in piercing the Irishman’s ear. Surprised but still on his feet, Macallister coolly exclaimed; “Hoot! The fellow, he’s deafened me!” Eventually steel, not lead or silver, brought down the notorious freebooter. Niel MacKay was killed in the early stages of the fight. Sir James, unaware of his friend’s death (and perhaps uncertain about his role in the attack), ordered his men “Let no man touch Niel MacKay!” When informed that MacKay had already fallen, Sinclair announced gravely; “Then spare none”.
The question of MacKay’s involvement remains open. Was it mere coincidence that Macallister’s men arrived at Thurso just behind him? There seems little reason for MacKay to contemplate such a desperate and despicable act as burning a church with its congregation still inside, particularly in his own region, where retribution would be swift and inevitable. Yet, when the going got rough for the freebooters in Thurso, they headed immediately for the house where MacKay was staying. They may have expected the help of MacKay and his men after aiding them against the Earl of Sutherland the previous year. Having realized that the bandits intended to burn them alive, the seething mob that poured out of Thurso in pursuit was probably not in the mood to listen to explanations of innocence. In any case MacKay and his men were of the professional fighting class, and once under attack would not have failed to respond in kind immediately.
None were spared to answer these questions. Only two of the bandits escaped the massacre, fleeing half a mile along the rocky sea-side cliffs to the village of Scrabster, where they were set upon and killed. In Robert MacKay’s 1829 history of the Clan MacKay, the author recalled seeing the place of their death marked by two large stones. The bodies of the rest were buried at the main entrance of the church (last used for services in 1832 and now a picturesque ruin). The remains of the caterans do not seem to have carried much respect with the locals; Robert MacKay records seeing in the possession of a Thurso merchant a remarkably large molar tooth recently pulled from one of the skulls. Niel MacKay’s mortal remains were another matter. Sir James was grief-stricken at the death of his friend who, moreover, had been his guest in the area. Sinclair ordered MacKay’s body to be interned in his own family plot, with the late chief’s coat-of-arms carved on the gravestone. It being the custom in the north at the time to take revenge for the death of any chief, Niel MacKay’s son, also named Niel, began the hunt for the men who brought down his father. The younger Niel killed a man closely involved, but the actual culprit eventually tired of being hunted and fled abroad.
With their days of victories under Montrose and Alisdair MacColla long behind them, the last of the ‘Redshanks’ met an ignoble death, their bones dumped in a pit outside the very church they intended to burn. In the following year, 1650, Montrose attempted a comeback from the Orkney Islands that lay within sight of Thurso across the northern sea. After crossing to the mainland with his hastily raised force of Orkney natives and Danish mercenaries (a poor substitute for MacColla’s Irish Brigade), Montrose was quickly defeated and sent on to Edinburgh to be hanged and quartered. His brilliant ally Alistair MacColla had already been killed at the 1647 battle of Knocknanuss in Ireland when his men made the fatal mistake of dispersing to loot the enemy’s baggage train after slashing their way through the Parliamentarian infantry. The massacre of Macallister and his men at Thurso brought a brutal end to the Redshanks in Scotland. It was not the end of Irish fighting men in Scotland, however. That would wait another hundred years for the end of Prince Charles Stewart’s failed rising of 1745-46.
Sources
Calder, James T: Sketch of the Civil and Traditional History of Caithness from the 10th Century, Wick, 1887
Gordon, Sir Robert: History of the House of Sutherland, Edinburgh, 1813
Haythornwaite, Philip: The English Civil War 1642-1651: An Illustrated Military History, Poole, Dorset, 1983
Hill, JM: Celtic Warfare 1595-1763, Edinburgh, 1986
Lenihan, Pádraig: “Celtic Warfare in the 1640s,” In John R Young (ed.), Celtic Dimensions of the British Civil Wars, Edinburgh, 1997, pp. 116-140
Lawson, John Parker: Historical Tales of the Wars of Scotland, Vol. I, Edinburgh, c.1850, pp. 326-28
MacKay, Robert: History of the House and Clan of MacKay, Edinburgh, 1829
Ó Ciardha, Éamonn: “Tories and Moss-Troopers in Scotland and Ireland in the Interregnum: a political dimension,” In, John R Young (ed.), Celtic Dimensions of the British Civil Wars, Edinburgh, 1997, pp. 141-163
Reid, Stuart: The Campaigns of Montrose: A Military History of the Civil War in Scotland, 1639 to 1646, Edinburgh, 1990
Reid, Stuart, and Graham Turner: Scots Armies of the English Civil Wars, Oxford, 1999
Stevenson, David: Scottish Covenanters and Irish Confederates, Belfast, 1981
Stradling, RA: The Spanish Monarchy and Irish Mercenaries, 1618-68, Dublin, 1994
This article was first published by Military History Online, November 8, 2007







