Andrew McGregor
AIS Special Report, March 3, 2019
Sudan’s embattled president, Omar al-Bashir, appeared to take a small step back from his authoritarian rule of Sudan on February 28 when he resigned as leader of the ruling National Congress Party (NCP – al-Mu’tamar al-Watani). However, his newly-appointed successor, Ahmad Muhammad Harun, is a long-time Bashir loyalist who, like his patron, is wanted by the International Criminal Court (ICC) and therefore has little interest in any regime change that could lead to arrest.
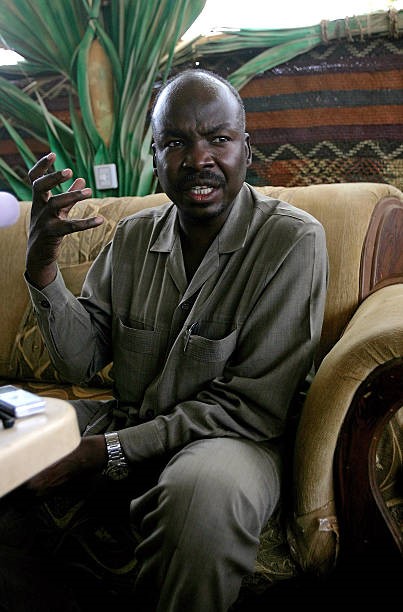 Ahmad Muhammad Harun as Governor of South Kordofan
Ahmad Muhammad Harun as Governor of South Kordofan
Harun, a 54-year-old trained as a lawyer, will serve as party chief on an interim basis until the next NCP convention. The promotion came only one week after Harun was appointed deputy chief of the party by al-Bashir and puts Harun in the unusual situation of automatically becoming the party’s next presidential candidate according to party rules (AFP, March 1, 2019). Of course Harun might be replaced at the party’s next convention, but the appointment signals that al-Bashir may be reconsidering his controversial bid to be re-elected president in 2020.
Harun’s promotion comes in the midst of a wave of administrative changes that accompanied the imposition of a state of emergency to deal with the continuing protests against the military-Islamist regime. All of the nation’s 18 provincial governors have been replaced by army officers or officials from the National Intelligence and Security Service (NISS).
Harun has long been the NCP’s point man on its most difficult files. His talent was spotted early, when he was made Sudan’s youngest minister of state (April 2003 – September 2005). His appointment as NCP chief shows the confidence al-Bashir has in Harun as someone who can keep a strong grip on the ruling party at a time when many members might be tempted to look at different political opportunities.
Harun first proved his usefulness to the regime in the 1990s, when he was involved in the organization and operations of the Murahileen, Arab militias living in the borderlands between north and south Sudan during the Second Sudanese Civil War (1983-2005). Harun and others were able to persuade Missiriya Arab tribesmen to raid and displace their long-time Ngok Dinka neighbors in an effort to control the massive oil reserves along the border between South Kordofan and Bahr al-Ghazal provinces. It was a blueprint that was later used in Darfur, where some Arab tribesmen were convinced by government agents that the looting and murder of their non-Arab Muslim neighbors was not only permissible but also well-rewarded.
The Darfur Security Desk was put under Harun’s control from April 2003 to September 2005, placing him in a command position over the activities of security services and pro-government militias. According to ICC chief prosecutor Luis Moreno Ocampo, it was during this time that Harun boasted he now had “all the power and authority to kill or forgive whoever in Darfur, for the sake of peace and security.” (Sudan Tribune, February 28, 2007). Harun later denied making the statement.
 Janjaweed Gunmen in Darfur, 2008 (Andrew Carter)
Janjaweed Gunmen in Darfur, 2008 (Andrew Carter)
According to Harun, the atrocities in Darfur were the work of rebel groups that had been unsuccessful in attempts to confront the Sudan Armed Forces (SAF) and its Janjaweed militias on the battlefield. In consequence, he alleged, the rebels targeted civilians while blaming the government for the atrocities in international forums and media: “They started putting pressure on civilians to move out of villages, they killed their children, women they abducted, they destroyed the infrastructure and means of people’s livelihood, and caused the mass migration of people into refugee camps” (Guardian, December 4, 2008).
ICC charges against Harun were first announced in February 2007 and an arrest warrant was issued in April of the same year. After the charges were laid, Harun made a public appearance to demand the ICC prosecutors first charge US President George W. Bush and former Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon with war crimes (Sudan Tribune, February 28, 2007).
Charges were filed at the same time against former Harun associate and Janjaweed commander ‘Ali Kushayb (a.k.a. ‘Ali Muhammad ‘Ali). President al-Bashir was charged with war crimes and crimes against humanity in 2008. Like the United States, Sudan is not a signatory to the ICC statutes and has refused all appeals to cooperate with the court.
Among the ICC charges were 51 counts of war crimes and crimes against humanity, including 14 counts of murder, ten counts of rape and the torture of 60 people (Telegraph, June 5, 2008). Most of the charges related to Khartoum’s ruthless counter-insurgency in Darfur during the period 2003 to 2005. Harun was Sudan’s interior minister at the time and responsible for internal security. In 2006, al-Bashir surprised many of those following the Darfur conflict by appointing Harun as Sudan’s new Minister of Humanitarian Affairs, putting Harun in charge of relief efforts for the hundreds of thousands displaced by his own activities in Darfur. In September 2007, Harun was placed in charge of an investigation of human rights abuses in Darfur.
Moreno Ocampo deplored Harun’s appointment to Minister of Humanitarian Affairs: “Formally, [Harun] shares responsibility for the safety and well-being of the displaced population. In reality, he joins in constant abuses against them” (IPSNews, February 6, 2009).
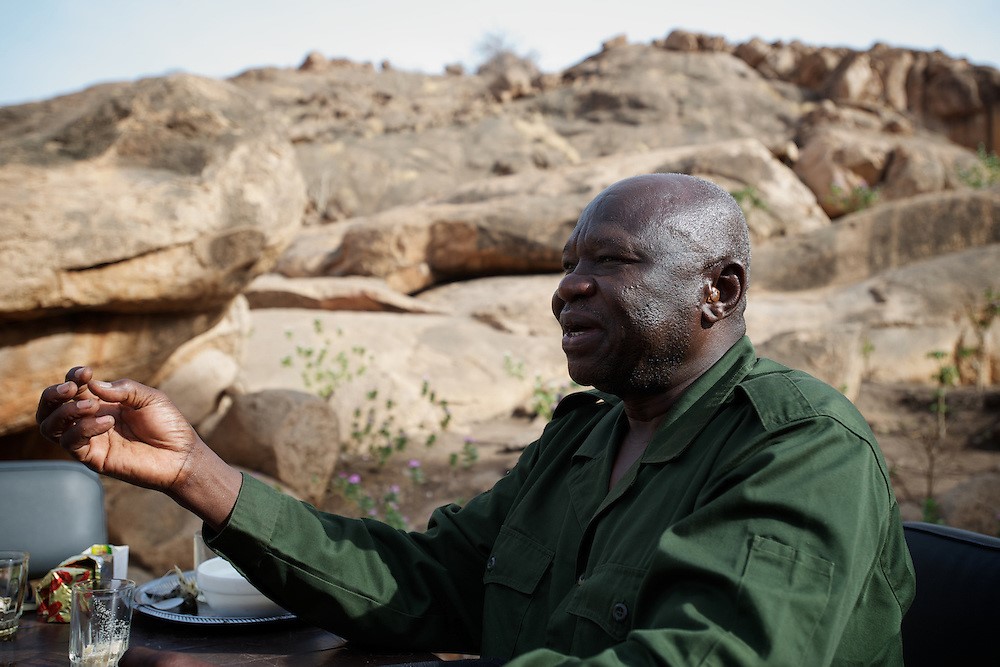 Commander ‘Abd al-Aziz al-Hilu (Paulo Nunes dos Santos/Polaris)
Commander ‘Abd al-Aziz al-Hilu (Paulo Nunes dos Santos/Polaris)
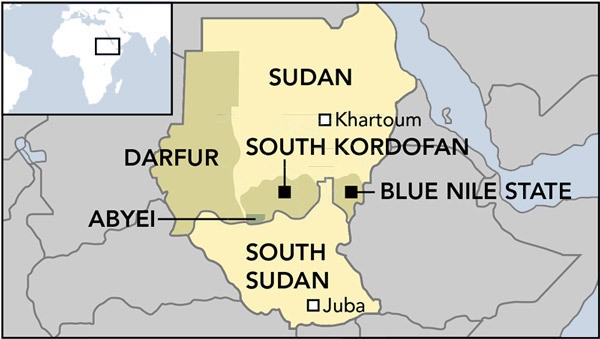
In May 2009, Harun was given a more familiar role as governor of South Kordofan province, where a rebellion was raging. Anti-government guerrilla actions were (and continue to be) led by the mainly Nuba fighters of the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement/Army – North (SPLM/A-N, which split-off from South Sudan’s SPLM/A when the south gained independence in July 2011). The movement is led by veteran opposition leader ‘Abd al-Aziz al-Hilu, who lost the May 2011 gubernatorial election to Harun (the NCP candidate) in a contest that was transparently rigged in the last hours when it appeared ‘Abd al-Aziz would be the certain winner. Another division of the SPLM/A-N operates in Blue Nile province; both sections are allied to the main rebel movements in Darfur.
 A spokesman for Darfur’s rebel Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) was unsurprised at the time that Harun had been appointed governor of South Kordofan: “Having orchestrated the Darfur genocide, Harun is the right choice for the Government of Sudan to complete the unfinished job to ethnically cleanse the Nuba People and bring in Arabs to occupy their lands” (Sudan Tribune, June 21, 2011).
A spokesman for Darfur’s rebel Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) was unsurprised at the time that Harun had been appointed governor of South Kordofan: “Having orchestrated the Darfur genocide, Harun is the right choice for the Government of Sudan to complete the unfinished job to ethnically cleanse the Nuba People and bring in Arabs to occupy their lands” (Sudan Tribune, June 21, 2011).
In April 2012, al-Jazeera obtained footage of Harun encouraging SAF troops in Southern Kordofan to take no prisoners during an offensive into rebel-held territory: “You must hand over the place clean. Swept, rubbed, crushed. Don’t bring them back alive. We have no space for them” (Al-Jazeera, April 1 2012).
For the moment, the rebel movements of Darfur, South Kordofan and Blue Nile state have extended a unilateral ceasefire, attempting to allow a popular uprising to continue without providing the regime with an opportunity to claim the protests are the work of rebel infiltrators (something security authorities have already done).
Harun maintains that everything he did in Darfur to preserve the regime and the state was his legal duty (Guardian, December 4, 2008). It is an approach al-Bashir will expect as the regime struggles to right itself in the midst of a popular uprising that threatens the president’s three-decade old rule.
